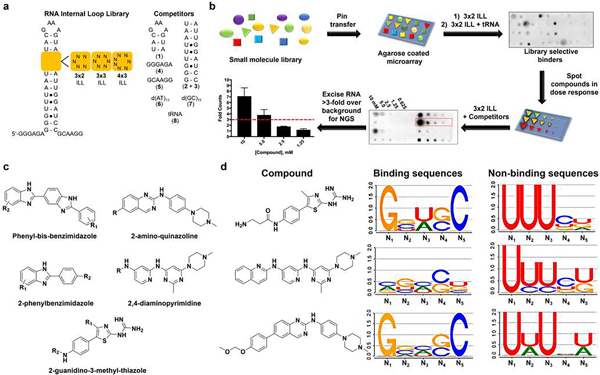
Fig. 1 |. Chemoinformatics and bioinformatics analysis of small molecules that bind RNA and the RNAs that bind small molecules.
a, RNA libraries used for screening the AstraZeneca collection. The 3 × 2 ILLs, 3 × 3 ILLs and 4 × 3 ILLs contain 1,024, 4,096 and 16,384 unique RNA sequences, respectively, totalling more than 63 million interactions probed by 2DCS. Competitor oligonucleotides used to restrict 2DCS selections to the randomized region are mimics of the hairpin (1), stem (2 + 3), 5′ tail (4), 3′ tail (5) as well as DNA (6, 7) and tRNA (8). b, Schematic of the AbsorbArray screening methodology14. NGS, next-generation sequencing. c, Tanimoto coefficient analysis identified five conserved classes of scaffolds, namely phenylbenzimidazoles, phenyl-bis-benzimidazoles, 2-aminoquinazolines, 4,6-diaminopyrimidines and 2-guanidinothiazoles, as RNA-biased binders. d, LOGOS analysis of the RNA sequences that bind compounds from the 3 × 2 ILLs; additional details can be found in the Supplementary Information. Examples are shown for the 2-guanidinothiazoles (C6), 4,6-diaminopyrimidine (C11) and 2-aminoquinazoline (C2), with compounds C6 and C2 being novel RNA-binding scaffolds. Nx denotes the position of the nucleotide in the randomized region, numbered in order from 5′ to 3′.