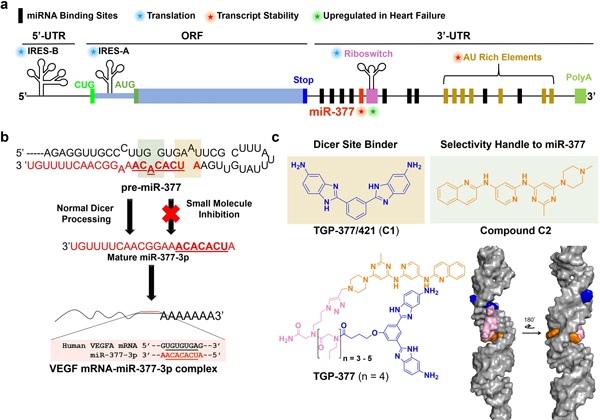
Fig. 3 |. Overview of Vegfa mRNA regulation, miR-377 pathway and targeting strategy.
a, Schematic of pathways that regulate VEGFA expression42. Of the known miRNAs that affect VEGFA, only miR-377 is upregulated post-ischemia. VegfA mRNA contains various regulatory elements, including (1) two IRESs that regulate translation, (2) a stress-responsive atypical riboswitch element that reacts to the binding of hnRNPL protein (activates translation) or interferon gamma-activated inhibitor of translation protein, (3) AU-rich elements (AREs) that control mRNA stability and (4) binding sites for miRNAs, including miR-377, miR-125a and miR-16, among others. b, Post-ischemic upregulation of miR-377 downregulates VEGFA, slowing growth and angiogenesis. A small molecule that binds pre-miR-377’s Dicer site (tan box, binding site for C1) and an adjacent bulge (green box, binding site for C2) can inhibit enzymatic processing and de-repress VEGFA, stimulating angiogenesis and proliferation. TargetScan-predicted binding site of miR-377’s seed sequence to Vegfa mRNA (aligned sequences are boxed); miR-377–3p indicates that the mature miRNA emanates from the 3′ end of the pre-miRNA. c, Design of a selective pre-miR-377 inhibitor by linking C1 (tan box in b indicates the binding site in pre-miR-377) and C2 (green box in b indicates the binding site in pre-miR-377) via compounds C1-COOH and C2-Ak, yielding TGP-377. MD simulations of the binding of TGP-377 to pre-miR-377 suggest that the compound intercalates into the two bulges with the linker threading through the major groove to support binding (bottom right). Both non-canonically paired adenines contribute to the stability of the complex by π−π stacking with the RNA-binding modules.