Figure 18.
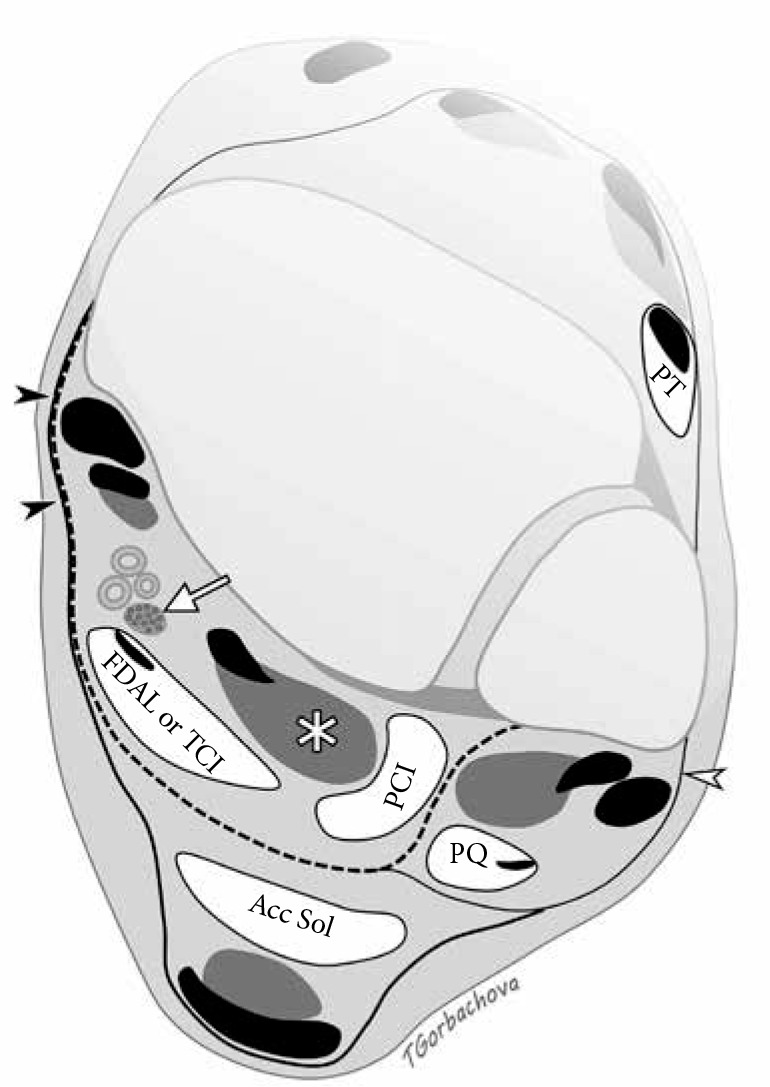
Accessory muscles of the ankle. Axial drawing illustrates location of common accessory muscles relative to the flexor hallucis longus (FHL) muscle (asterisk), deep aponeurosis (dashed line), and neurovascular bundle including posterior tibial nerve (arrow). Flexor retinaculum (black arrowheads) is formed by fusion of the superficial and deep aponeurosis. Accessory soleus muscle (Acc Sol) is located superficially to the deep aponeurosis. Peroneal calcaneus internus muscle is situated laterally to FHL. Both flexor digitorum accessorius longus and tibiocalcaneus internus muscles are located deep to the aponeu- rosis and posteromedial to the FHL; they can be differentiated by tracing their insertions distally. Peroneus quartus travels posteromedial to the peroneal tendons encircled by superior peroneal retinaculum (white arrowhead). Pero- neus tertius is located in the anterior compartment
