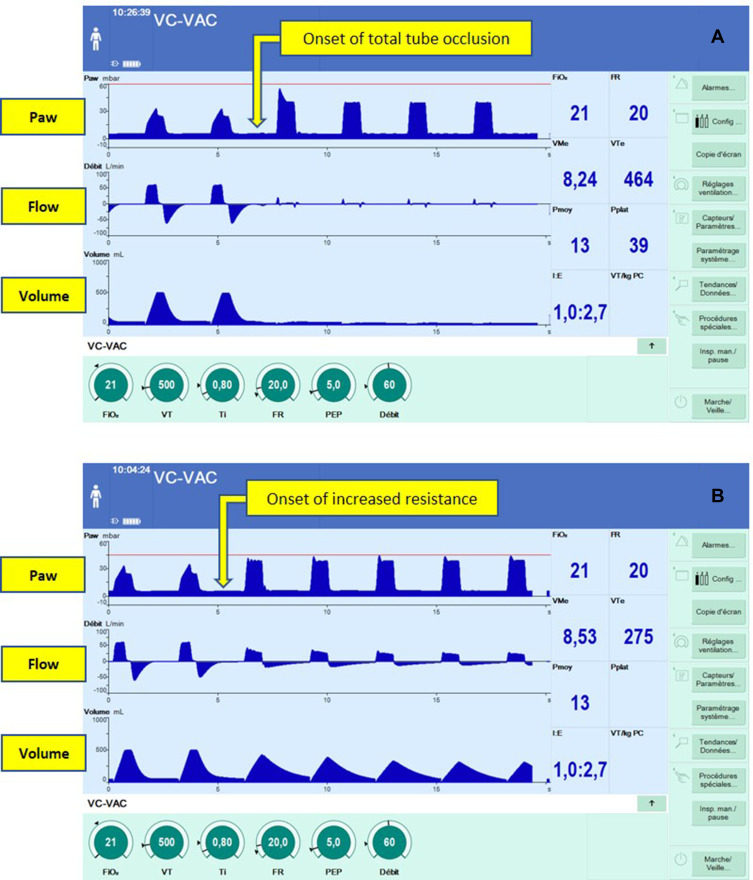
Figure 1.
Screenshots illustrating the activation of the pressure limitation algorithm. In both situations (A and B) the ventilator was set in volume-controlled mode with the following parameters: tidal volume 500 mL, RR 20/min, PEEP 5 mbar, inspiratory flow 60 L/min, inspiratory time 0.8 seconds. High airway pressure alarm (red line) was set to 60 mbar (A) or 45 mbar (B). A complete (A) or incomplete (B) obstruction were simulated by a direct maneuver exerted on the tube, triggering the activation of the algorithm. This activation was associated with changes in pressure and flow curves shape, adopting from that moment the shape usually observed in pressure support mode (target of pressure and decelerating flow). Note that delivered volume was lower (A) or absent (B) compared to the one prescribed, without an alarm being triggered.