Figure 1.
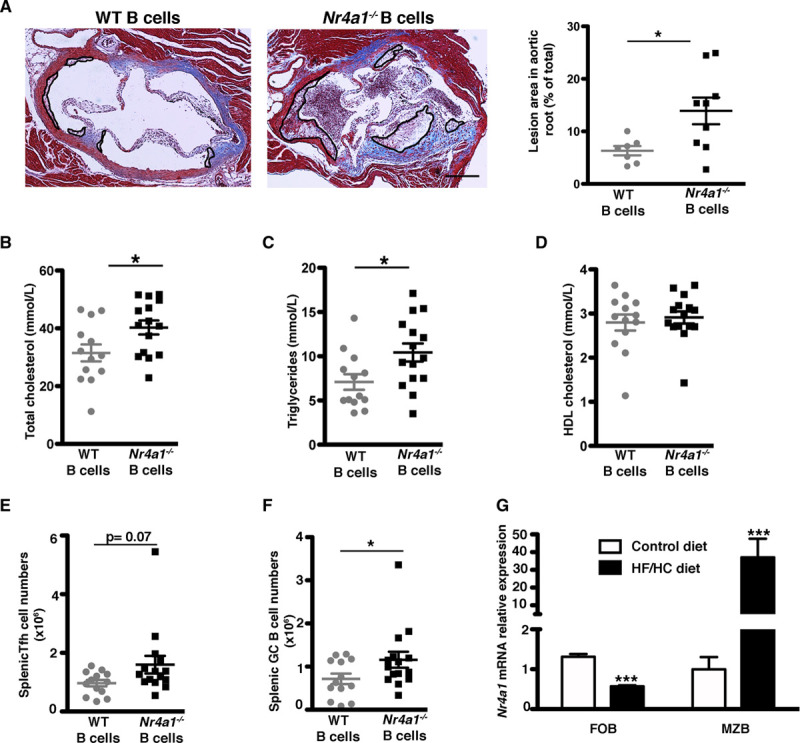
Nr4a1 (nerve growth factor IB) deletion in B cells increases atherosclerosis development. Ldlr−/− mice were transplanted with a mixed chimera containing 80% µMT +20% WT (wild type; for reconstitution with WT B cells) or 20% Nr4a1−/− (for reconstitution with Nr4a1−/− B cells) BM and fed a high-fat/high-cholesterol (HF/HC) diet for 8 wk (A–F). A, Representative Masson trichrome staining and quantification of atherosclerotic plaques in aortic roots (each symbol represents one mouse, and the horizontal bars are group mean±SEM with n=7 and n=9, respectively, in each group). Original magnification, ×10. Scale bars=500 μm. B–D, Total plasma cholesterol, triglycerides, and HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels. E and F, Total numbers of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells (CD3+ CD4+ CD44+ CD62L− ICOS+ CXCR5+ PD1+) and germinal center (GC) B cells (B220+ CD19+ CD95+ GL7+; n=13–15 in each group). G, Nr4a1 relative expression in sorted marginal zone B (MZB) and follicular B (FOB) cells from Ldlr−/− mice fed a standard laboratory or HF/HC diet for 8 wk (n=3–4 in each group). For A–G, 2-tailed unpaired Student t test or 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis, *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001. CD indicates cluster of differentiation; CXCR5, C-X-C chemokyne receptor-5; ICOS, inducible T-cell coestimulator; and PD1, programmed cell death protein 1.
