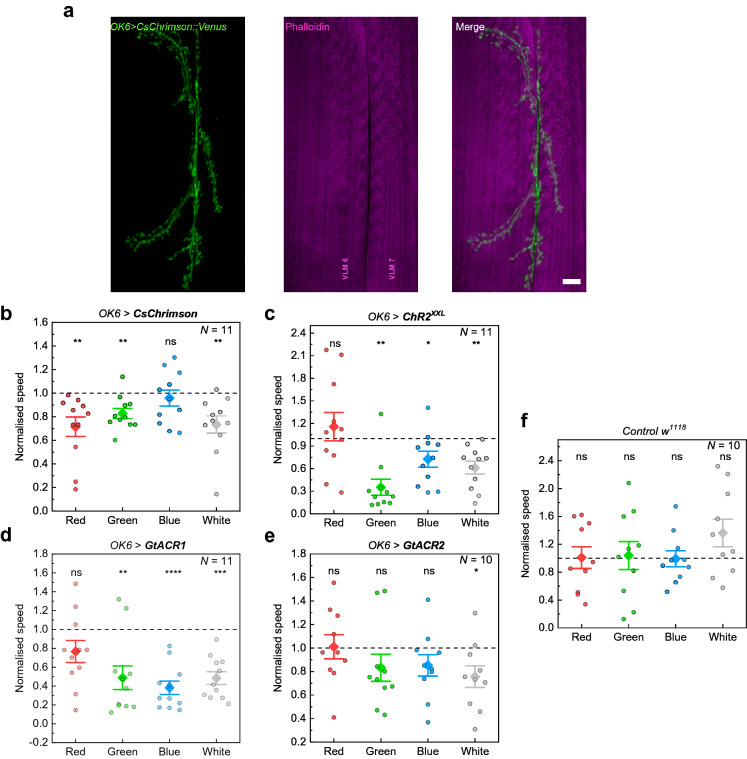
Figure 2.
Behavioural response of larvae expressing different light-sensitive ion channels in motor neurons (OK6-GAL4) to optogenetic stimulation with the Honor 8 smartphone display. (a) Motoneuronal expression of Chrimson::Venus obtained by antibody staining against the photoprotein (green). Phalloidin stained ventral longitudinal muscles (VLM) depicted in magenta. Scale bar: 10 µm. (b)–(f) Larval responses to illumination with different colours in temporal sequences of red (R), green (G), blue (B), and white (W) light with intermediate black periods (Supplementary Fig. S3). Data show the speed of the larvae normalised to the previous black period as obtained by tracking the head (see Methods). (b) Neuronal activation of OK6 > CsChrimson larvae. Stimulation period of 20 s with 60 s of rest (black period). (c) Neuronal activation using OK6 > ChR2XXL. Stimulation period: 10 s; black period: 150 s. (d) Neuronal silencing using OK6 > GtACR1. Stimulation period: 20 s; black period: 60 s. (e) Neuronal silencing using OK6 > GtACR2. Stimulation period: 30 s; black period: 60 s. (f) Normalised speed of w1118 control larvae. Stimulation period: 20 s; black period: 30 s. N: number of larvae; whiskers: s.e.m.; diamonds: mean. Significance calculated via one-sample two-tailed t-test: ns: not significant (p > 0.05), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.