Figure 1.
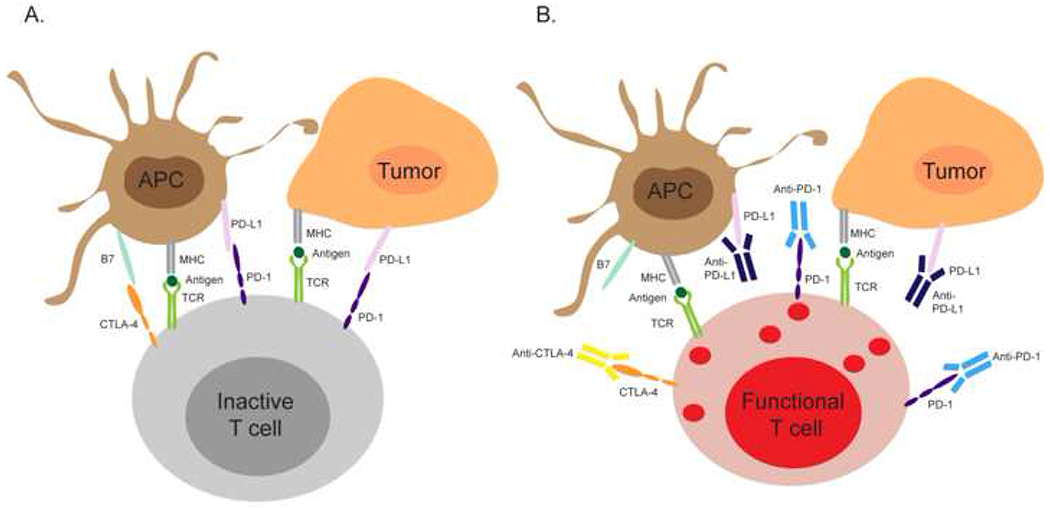
Immune checkpoint inhibitors reinvigorate antitumor immune responses.(A) Cytotoxic T cells in the tumor microenvironments express high level of inhibitory receptors such as CTLA-4 and PD-1. In the absence of immune checkpoint inhibitors, ligation of CTLA-4 and PD-1 by B7 or PD-L1 expressed by antigen presenting cells or tumor cells dampens the cytotoxic functions of T cells and inhibits their antitumor activity. (B) Anti-CTLA-4, anti-PD-1, and anti-PD-L1 can bind CTLA-4, PD-1, and PD-L1 and prevent the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4/B7 interactions, which restore the antitumor functions of cytotoxic T cells. Abbreviations: APC, antigen presenting cell; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T-cell receptor; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand-1; B7, B7 protein.
