Figure 2: Cerebellar neurochemical levels are altered in hemizygous Q135 mice.
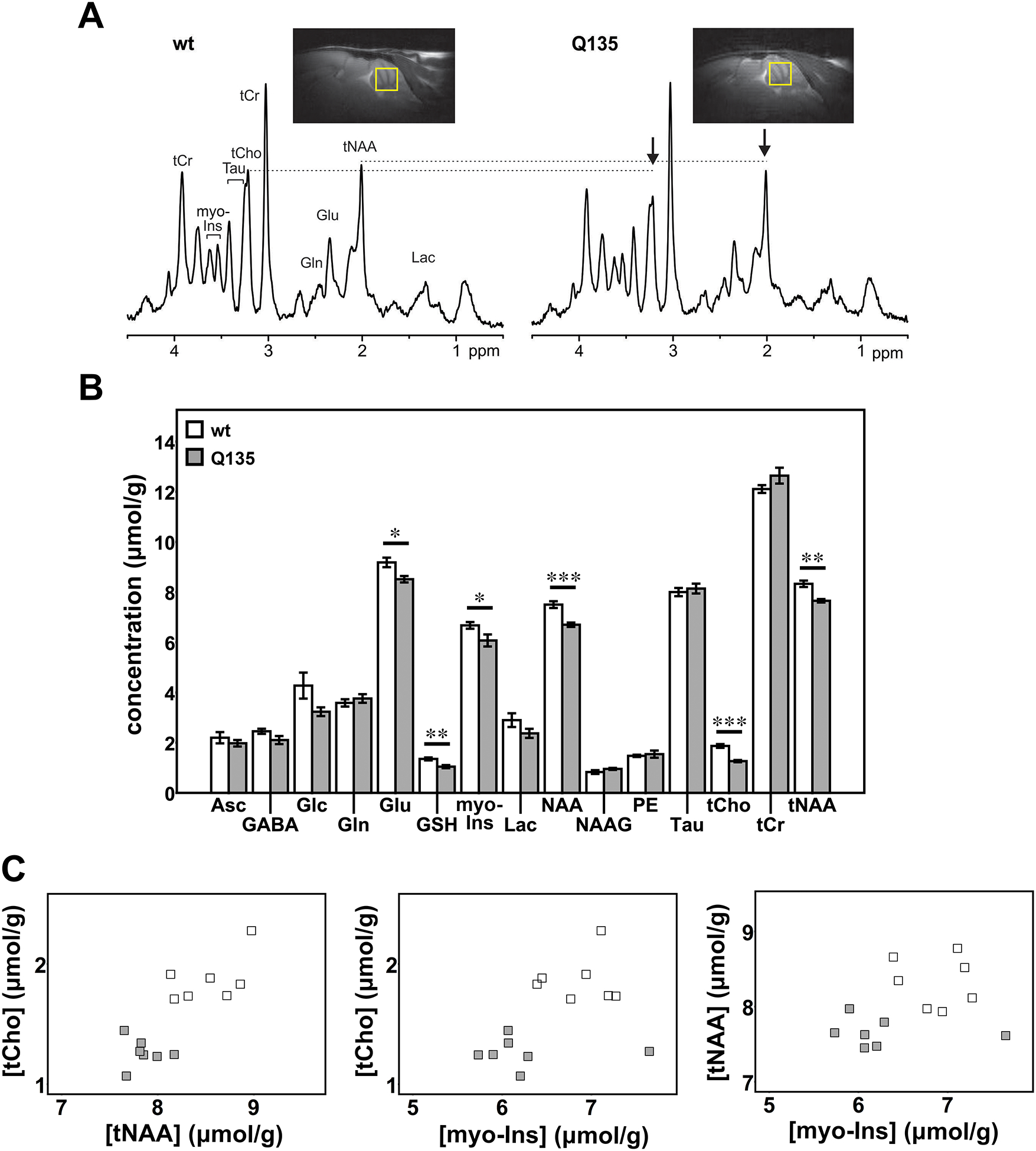
A) Representative localized proton MR spectra and midsagittal T2-weighted images of a Q135 and a wt littermate mouse. The most prominent neurochemical abnormalities, namely lower tCho and tNAA in Q135 compared to wt mice, are denoted in the spectra by arrows. B) Cerebellar neurochemical profiles of Q135 mice (N=7, grey bars) and wt littermates (N=7, white bars). Bars represent average chemical concentration ± SEM. Comparison between mouse genotypes was performed using Student’s t-test and statistical significance is indicated as: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001. C) Separation of Q135 mice (grey squares) from controls (white squares) by plotting two altered metabolites against each other.
