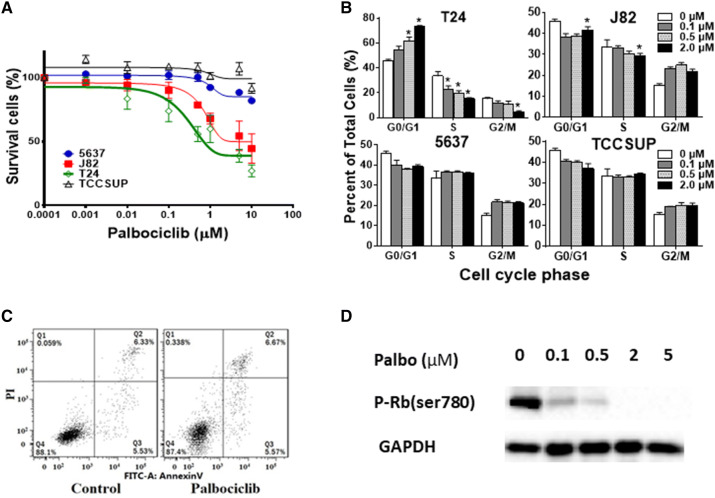
Fig. 2.
Effect of CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib on bladder cancer cell lines. a Dose response curves of bladder cancer cell lines treated with palbociclib. T24, J82, TCCSUP, and 5637 cells were grown in 96-well plates and incubated for 72 h at 37 °C with increasing concentrations of palbociclib (1–10,000 nmol/L). The number of viable cells were determined by the MTS cell viability assay. b Cell cycle analysis of bladder cancer cell lines treated with palbociclib. Cells were treated with different concentrations of palbociclib (0.1, 0.5, 2 μM) or DMSO (Ctrl) for 48 h. Cell cycle progression was determined by flow cytometry. Columns mean; bars SD; n = 3. *p < 0.05. The percentage of S-phase was significantly decreased, and G1-phase was significantly increased in a dose-dependent manner in T24 and J82 cells; no significant change of cell cycle was detected in 5627 and TCCSUP cells. c Apoptosis analysis in T24 cells. Cells were treated with 2 μM palbociclib or DMSO (Ctrl) for 48 h and stained with Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI). One representative flow cytometry result was presented. Percentages of early (Annexin V+/PI−, Q3) and late apoptoses (Annexin V+/PI+, Q2) were indicated. No significant changes were observed, suggesting that palbociclib rarely induces apoptosis even in the sensitive T24 cells. d Western blot analysis of phospho-Rb protein in bladder cancer cell line T24. Cells were treated with palbociclib for 48 h with indicated palbociclib concentrations. p-Rb protein was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner