Figure 4.
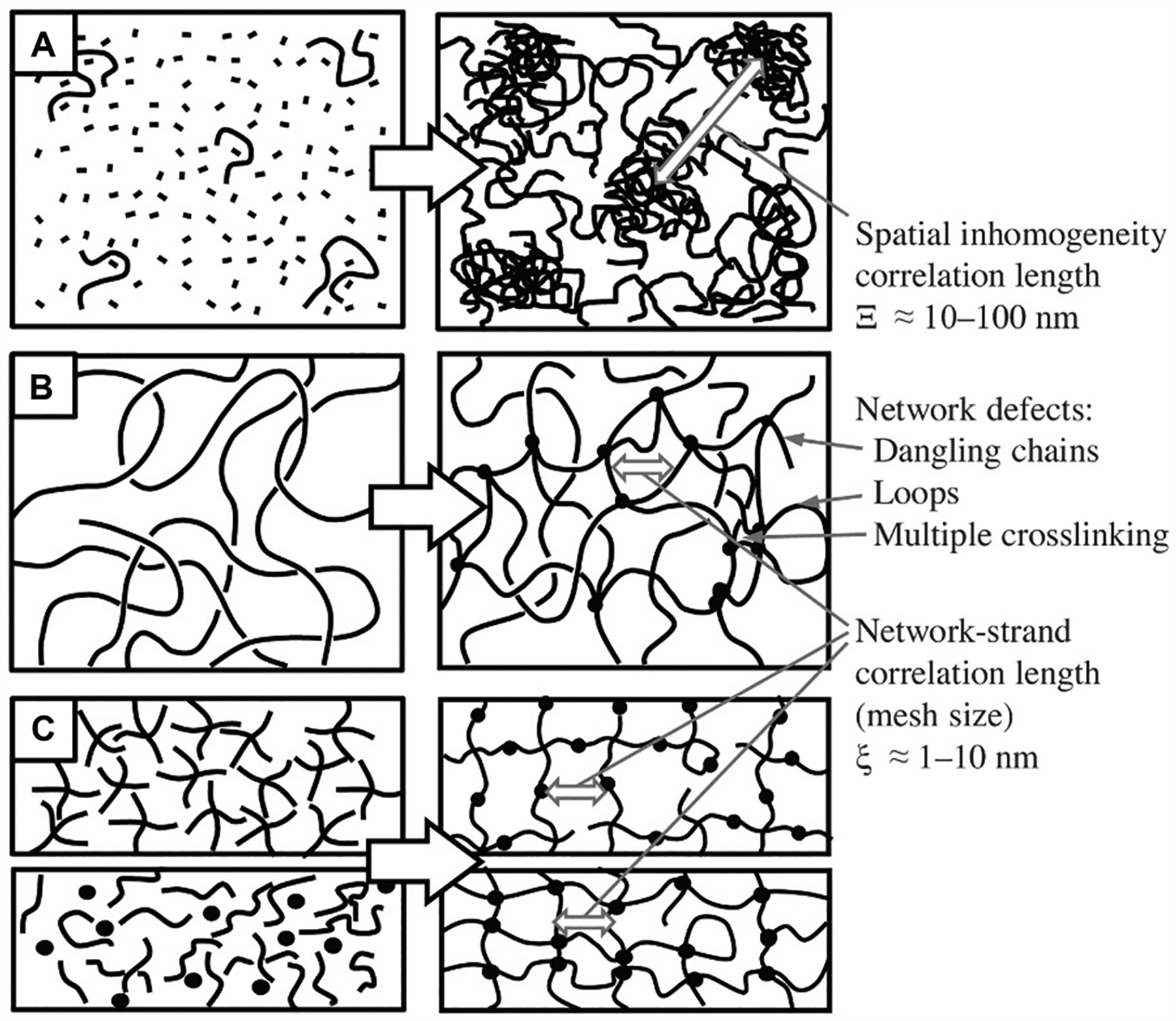
Depiction of hydrogel network formation depending on cross-linking mechanism and the resulting degree of inhomogeneity. (A) Free-radical chain growth polymerization of monomers and cross-linkers leading to spatial inhomogeneity within the network architecture. (B) Network formation via cross-linking of reactive functional side groups of the polymer chains in a semidilute solution, leading to local inhomogeneity. (C) Orthogonal step-growth polymerization resulting in a mostly ordered, homogeneous network. Reproduced with permission from ref 78. Copyright 2017 Elsevier.
