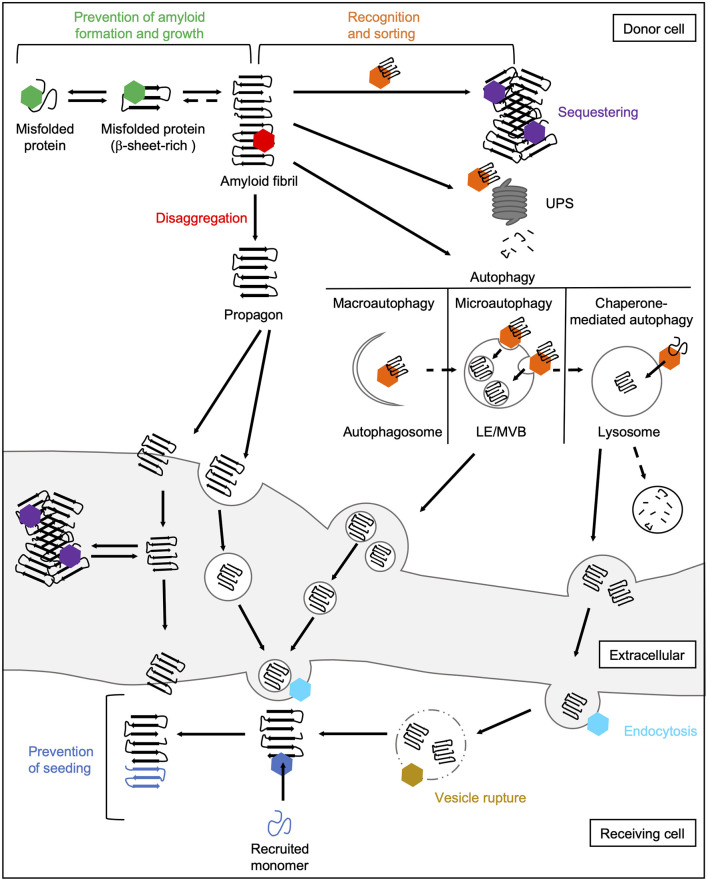
Figure 4.
Chaperone interactions during prion-like propagation of disease proteins. The folding and refolding activity of chaperones helps destabilized or misfolded protein species to resume their native state. These transient interactions with misfolded proteins or small oligomers prevent the formation of a seeding-competent propagon (green hexamer). In contrast, the Hsp70 disaggregation machinery can fragment large fibrils leading to the formation of smaller seeding- and spreading-competent species (red hexamer). Chaperones also recognize and sort terminally misfolded forms (orange hexamer) and either mediate their sequestration into an inert deposit (purple hexamer) or deliver them to degradation pathways. Sequestration may reduce the accessibility of fibril ends and thus prevent the further incorporation of native proteins into the amyloid fibril. Extracellular chaperones can also sequester amyloidogenic proteins into large deposits making uptake into receiving cells more difficult. The delivery of amyloidogenic proteins to macroautophagic isolation membranes for their selective clearance is mediated by HSC70 and an sHsp, HSPB8, together with the NEF BAG3 (Gamerdinger et al., 2009). In microautophagy, constitutively expressed HSC70 targets substrates to LEs/MVBs (Sahu et al., 2011). In CMA, HSC70 translocates clients directly across the lysosomal membrane (Tekirdag and Maria Cuervo, 2018). Lysosomes and MVBs can fuse with the plasma membrane releasing either free proteins or exosomes to the extracellular space. In the receiving cell, HSC70 and DNAJC6 are involved in the internalization of misfolded proteins via clathrin-mediated endocytosis by uncoating clathrin-coated vesicles (light blue hexamer; Sousa and Lafer, 2015). By rupturing the endosomal membrane, disease-associated proteins are released from the endocytic vesicle into the cytosol (Flavin et al., 2017), which might be prevented by lysosomal or cytosolic Hsps (yellow hexamer). In the cytosol of the receiving cell, chaperones can finally interfere with the seeding of naïve species by the released propagon (dark blue hexamer). CMA, chaperone-mediated autophagy; LE, late endosome; MVB, multivesicular body; NEF, nucleotide exchange factor; UPS, ubiquitin-proteasome system.