Figure 6.
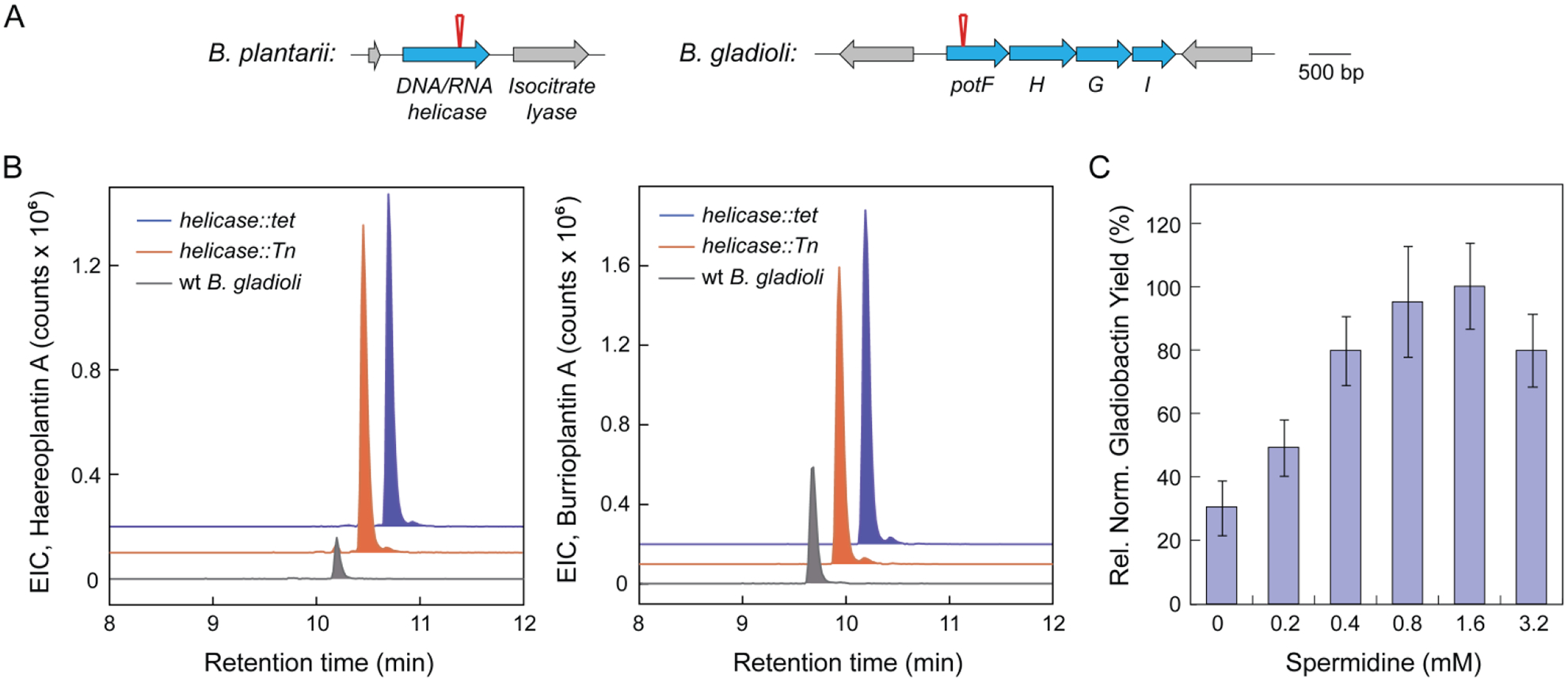
Identification of Tn insertion sites in the haereoplantin, burrioplantin, and gladiobactin overproducers. (A) Tn insertion in B. plantarii occurs in a DNA/RNA helicase, as indicated by the red pin. In B. gladioli, Tn insertion occurred into potF (red pin) in the pot operon. (B) Disruption of the DNA/RNA helicase recapitulates the effect of Tn insertion. (Left) Extracted ion chromatograms of haereoplantin A in wt B. plantarii (gray trace), the helicase::Tn mutant (red), and the helicase deletion mutant (helicase::tet, blue). (Right) Extracted ion chromatograms of burrioplantin A in wt B. plantarii (gray), Tn mutant (red), and helicase deletion mutant (blue). (C) Induction of gladiobactin synthesis by spermidine. Shown is cell density-normalized relative quantification of gladiobactin A as a function of exogenous spermidine concentrations. The relative levels of gladiobactin in each culture supernatant were determined from integration of the gladiobactin peak observed in extracted-ion chromatograms. The average from two independent measurements is reported. Error bars represent standard error.
