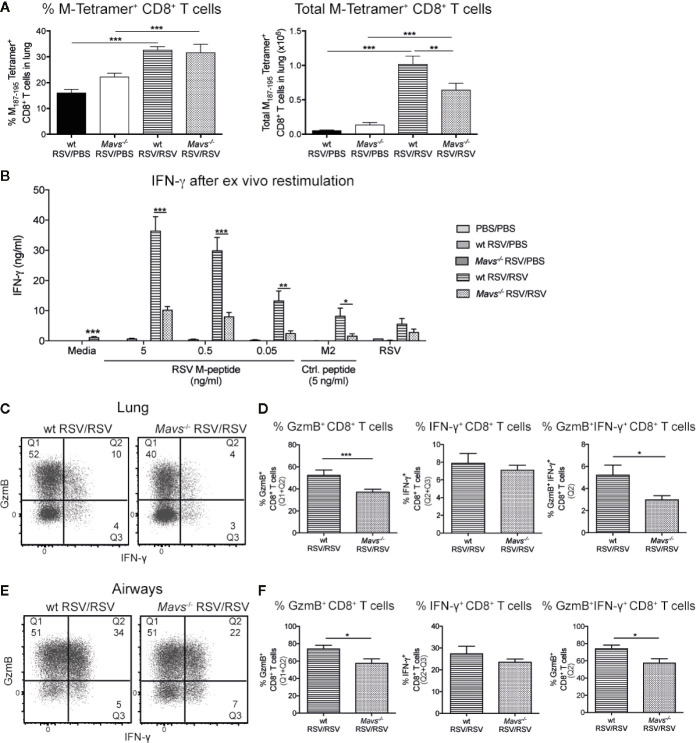
Figure 5.
Less potent RSV-specific GzmB and IFN-γ/GzmB producing CD8+ T cells in Mavs−/− mice during secondary RSV infection. CD8+ T cells contribute significantly to IFN-γ; and Granzyme B (GzmB) production during secondary infection with RSV. (A) Quantification of frequencies and total M187-195 tetramer positive CD8+ T cells in lungs, on day 4 post RSV re-infection. (B) IFN-γ produced by lung cells after ex vivo stimulation with the immunodominant RSV peptide CD8+ T cell M187-195, the irrelevant peptide M282-90 as control (Ctrl) and RSV (MOI 1). IFN-γ protein levels were determined by ELISA after 72 h. (C) Representative flow cytometry plots of CD8+ T cells expressing GzmB and/or IFN-γ in the lung tissue of wt and Mavs−/− mice re-challenged with RSV (RSV/RSV). The frequencies of GzmB and/or IFN-γ producing cells of the CD8+ T cells in the lung are shown in the quadrants and quantified in (D). (E) Representative flow cytometry plots of CD8+ T cells expressing GzmB and/or IFN-γ in the airways of wt and Mavs−/− mice re-challenged with RSV (RSV/RSV). The numbers in the quadrants represent the frequencies of GzmB and/or IFN-γ producing cells of the CD8+ T cells in the airways and this is quantified in (F). Data are represented as mean ± SEM and pooled from two independent experiments with four to five mice per group (n = 5–10). In addition, in (B) each data point was determined as a mean of duplicate wells. Statistical significances of differences between groups were determined by unpaired Student’s t test. In (B) only difference between RSV re-infected groups are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.