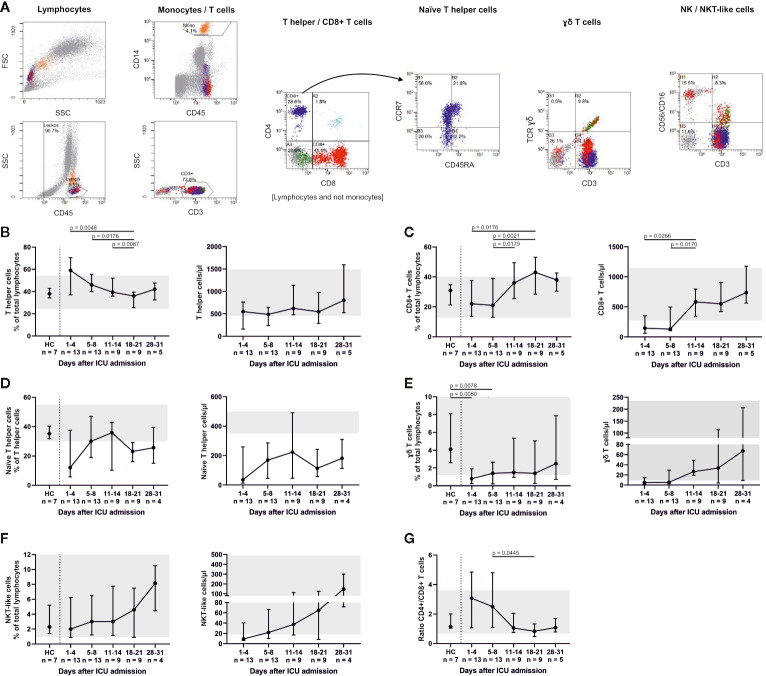
Figure 3.
T cell subsets were differentiated by flow cytometry (representative gating, A) and demonstrated considerably reduced CD3+ CD8+ T cells and CD3+ CD4+ CCR7+ CD45RA+ naïve T helper cells. Both fractions slowly increased during treatment with a maximum between days 11 and 21. Absolute numbers of naïve T helper cells remained far below the reference range throughout ICU therapy (B–D). CD3+ γδ+ T cells were also significantly reduced at admission and only partly replenished (E), whereas CD3+ CD56/CD16+ natural killer T (NKT)-like cells increased towards the end of ICU treatment (F). A declining CD4+/CD8+ ratio reflected these changes (G). Overall, these findings suggest that severe COVID-19-induced ARDS was accompanied by a T cell response with a delayed cytotoxic reaction. Relative cell counts on the left of each pair of graphs are contrasted with absolute cell numbers on the right, respectively. FSC, forward scatter; SSC, side scatter; HC, healthy controls; TCR, T cell receptor.