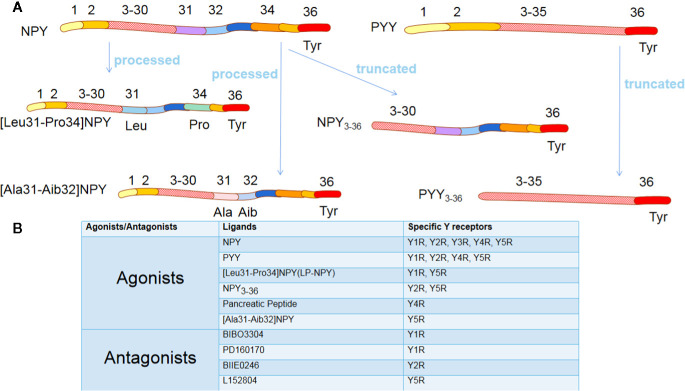
Figure 1.
The agonists and antagonists of Y receptors. (A) NPY and PYY are processed into different ligands. Although these ligands have a similar amino acid composition to NPY/PYY, when the two amino acid residues of NPY/PYY are replaced or truncated, it significantly changes their affinity for different Y receptor subtypes. (B) The most commonly used agonists and antagonists specific for different Y receptor subtypes. NPY, neuropeptide Y; PYY, peptide YY; Tyr, Tyrosine; Leu, Leucine; Pro, Proline; Ala, Alanine; Aib, 2-aminoisobutyric acid.