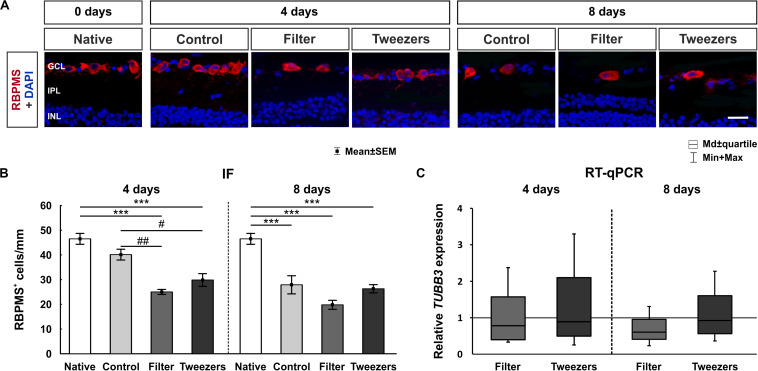
FIGURE 6.
Evaluation of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). (A) RGCs were labeled with RNA-binding protein with multiple splicing (RBPMS) (red) and cell nuclei with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). (B) The amount of RBPMS+ cells in control retinas was comparable to that in native ones. The number of RGCs was significantly reduced in both novel methods, filter (p < 0.001) and tweezers (p < 0.001), compared to the native method at 4 days. A significant loss of RGCs was noted in filter (p = 0.002) and tweezers samples (p = 0.03) compared to control ones. At 8 days, fewer RGCs were visible for all three groups control, filter, and tweezers compared to those in native samples (all: p < 0.001). (C) No differences in the TUBB3 mRNA expression levels were detected between all groups at 4 and 8 days. GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer. Scale bar: 20 μm, values are mean ± SEM for immunofluorescence (IF) and median ± quartile + min/max for quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). IF: n = 9–10/group; RT-qPCR: n = 5/group. ***p < 0.001 vs. native group; #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 vs. controls.