Figure 1.
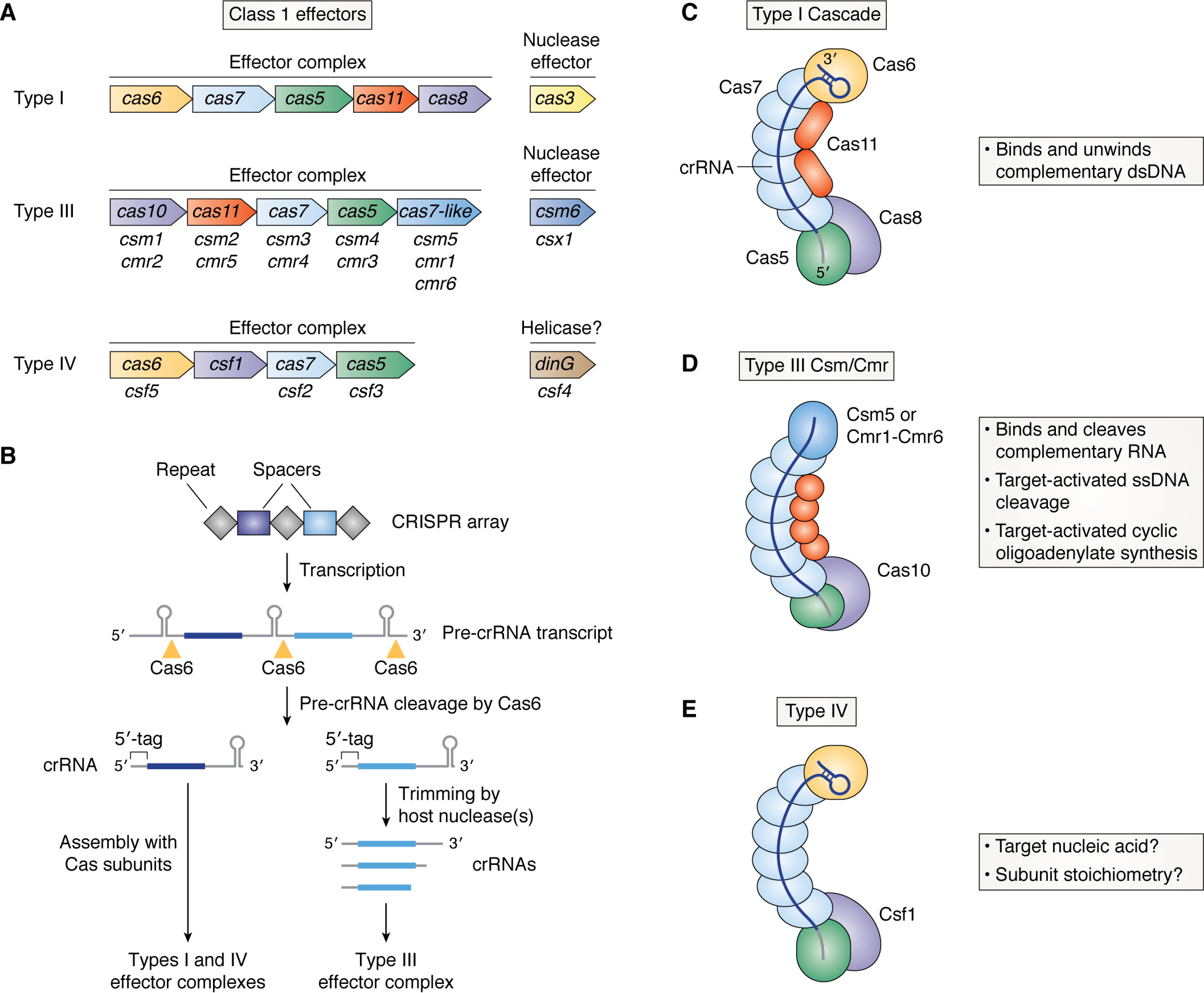
Effector complex architecture and crRNA biogenesis in Class 1 CRISPR-Cas systems. A, Cas protein composition of Class 1 effector complexes and their associated nuclease effectors. Subunits that are analogous between the different types are shown with the same color. Type III– and IV–specific names for Cas7, Cas5, Cas6, and Cas11 subunits are also shown below the canonical subunit names. B, biogenesis of Class 1 crRNAs. Transcription across a CRISPR array (repeat sequences are shown as gray diamonds, and unique spacers are shown as dark and light blue rectangles) leads to production of a pre-crRNA transcript that is then cleaved by Cas6 into individual guide molecules. Each crRNA has a 5′-tag that is derived from the repeat sequence. Individual guides are then directly incorporated into Type I and IV complexes or trimmed at their 3′ end by host nucleases before assembly with Type III effector subunits. C, architecture and enzymatic activities of the Type I crRNA-guided effector complex, Cascade. Subunits are shown with the same color scheme as in A. The crRNA is shown with the same color scheme as in B. D, as in C but for the Type III effector complex, Csm (subtypes III-A/D/E/F) or Cmr (subtypes III-B/C). Subunits unique to Type III systems (Cas10 and either Csm5 or Cmr1/6) are labeled. E, as in C but for the Type IV effector complex. The subunit unique to the Type IV system (Csf1) is labeled. Type IV complexes contain a crRNA assembled with Cas7, Cas6, and Csf1, but their enzymatic activity, precise stoichiometry, and structure are not yet known.
