Figure 4.
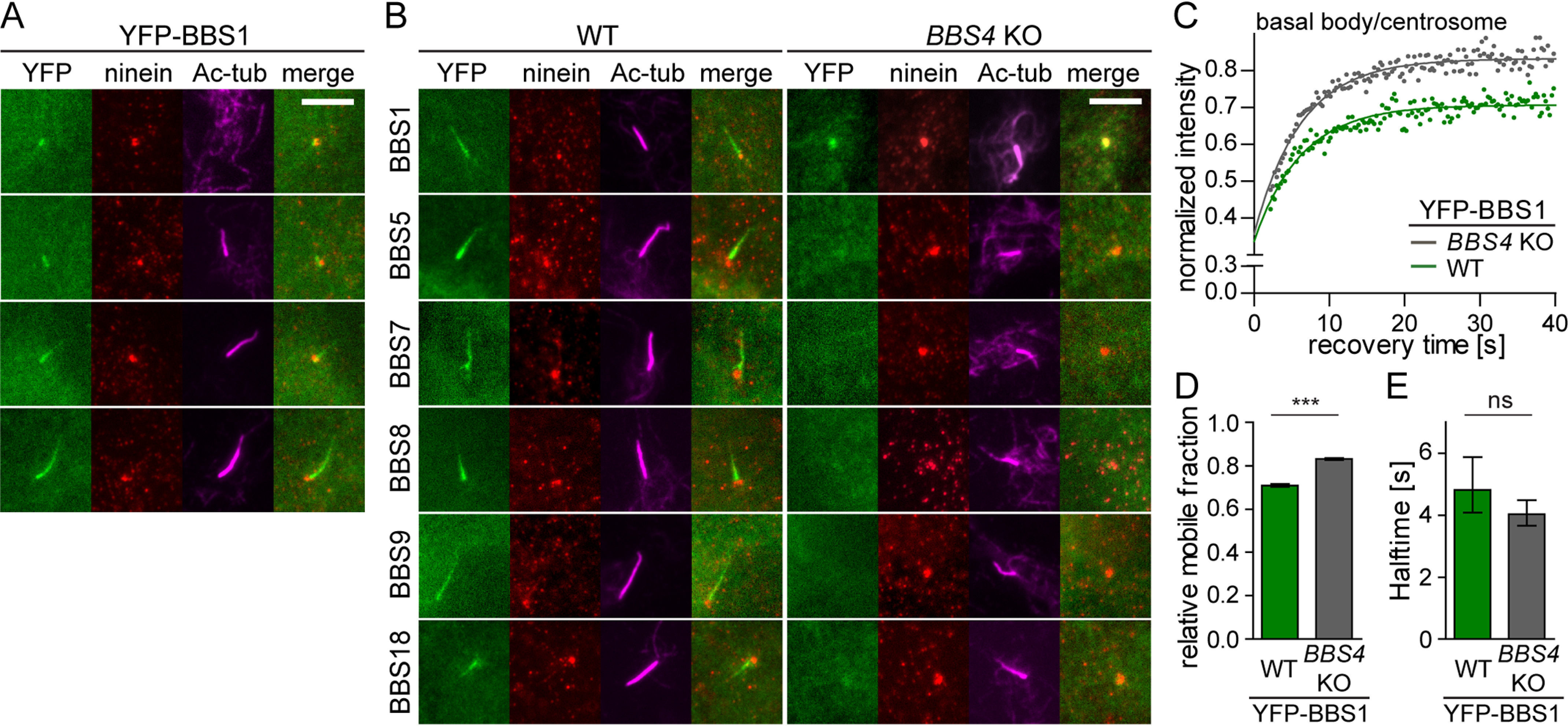
BBS1 acts as a gatekeeper at the basal body to facilitate BBSome completion and its entry to cilia. A, YFP-tagged BBS1 transits through the centrosome into the ciliary base and the cilia in WT RPE1 cells. Ninein and acetylated tubulin staining visualizes the centrosome and cilia, respectively. Scale bar, 5 μm. B, YFP-tagged BBSome subunits localize to the primary cilia (Ac-tub) in WT RPE1 cell lines. YFP-BBS1 localizes to the centrosome (Ninein) in the BBS4 KO cells, whereas the other YFP-tagged BBSome subunits are diffused in the cytoplasm. Scale bar, 5 μm. C, FRAP analysis of the dynamic turnover of the YFP-BBS1 at the centrosome or basal body in WT and BBS4 KO RPE1 cells. Recovery curves were fitted using one-phase association fit, and the means of 20–30 FRAP measurements from three independent experiments are shown. Estimated half-times t½ and immobile fractions are shown in Table S4. D, bar graph depicts the relative mobile fraction of YFP-BBS1 in WT and BBS4 KO cells extracted from FRAP analysis in C. YFP-BBS1 has a greater mobile fraction in BBS4 KO than in WT RPE1 cells. Means of 20–30 measurements from three independent experiments are shown. Error bars, 95% confidence interval. ***, p < 0.001. E, bar graph depicts the recovery half-time of YFP-BBS1 in WT and BBS4 KO cells obtained from FRAP analysis (C). Means of 20–30 measurements from three independent experiments are shown. Error bars, 95% confidence interval. ns, not significant; p > 0.5.
