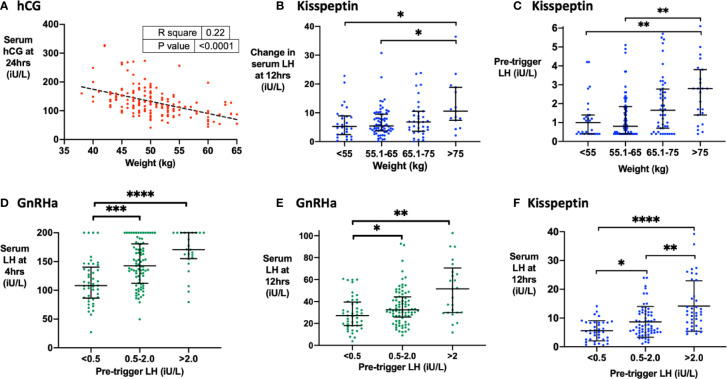
Figure 2.
Factors that determine hCG levels after hCG trigger and the LH level after GnRHa or kisspeptin. (A) Pre-treatment weight (kg) negatively predicted serum hCG level at 24 h (iU/L) after hCG trigger by simple linear regression (n = 161). Serum hCG at 24 h (iU/L) = −4.21 X body weight (kg) + 343.1, r2 = 0.22, P < 0.0001. (B) Median (IQR) of change in serum LH at 12 h (iU/L) by categories of body weight (kg) after kisspeptin (n = 141). Categories were compared by the Kruskal-Wallis test with post-hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test. (C) Median (IQR) of pre-trigger serum LH (iU/L) by categories of weight (kg) after kisspeptin (n = 173). Categories were compared by the Kruskal-Wallis test with post-hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test. Three outliers were not shown on the graph. (D) Median (IQR) of serum LH at 4 h (iU/L) by categories of pre-trigger LH after GnRHa (n = 150). Categories were compared by the Kruskal-Wallis test with post-hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test. (E) Median (IQR) of serum LH at 12 h (iU/L) by categories of pre-trigger LH after GnRHa is presented (n = 151). Categories were compared by the Kruskal-Wallis test with post-hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test. Two outliers were not shown on the graph. (F) Median (IQR) of serum LH at 12 h (iU/L) by categories of pre-trigger LH after kisspeptin (n = 142). Categories were compared by Kruskal-Wallis test with post-hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.