FIG 5.
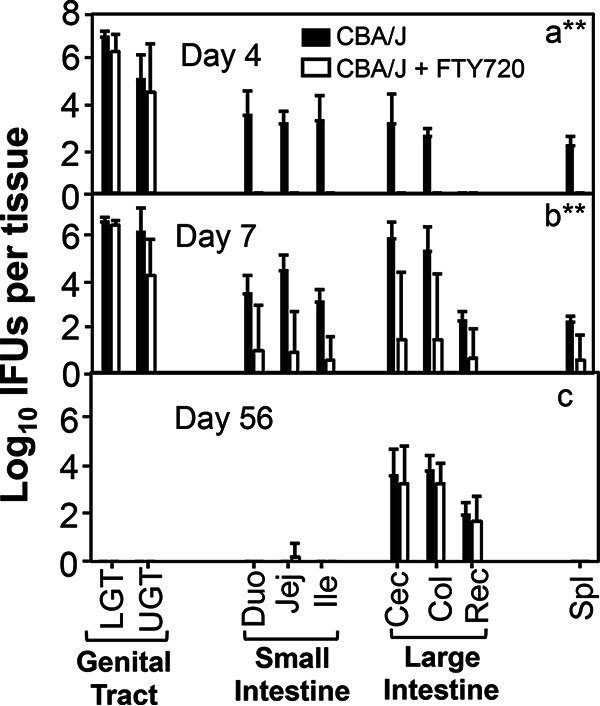
FTY720 significantly delayed genital Chlamydia spreading to the gastrointestinal tract and systemically in CBA/J mice. Groups of female CBA/J mice (n = 4) infected intravaginally with Chlamydia were treated without (solid bar) or with (open bar) FTY720. On days 4 (a), 7 (b), and 56 (c), groups of mice (n = 4) were sacrificed for measuring live chlamydial organisms from different tissues as shown along the x axis. The tissues include lower genital (LGT) and upper genital (UGT) tracts, small intestine duodenum (Duo), Jejunum (Jej), ilium (Ili), and large intestine tissues cecum (Cec), colon (Col), rectum (Rec), as well as spleen tissue (Spl). The live chlamydial organism titers were expressed as log10 IFUs per tissue (y axis). Note that FTY720 treatment significantly reduced spreading of genital Chlamydia to the gastrointestinal tract tissue on days 4 and 7 but not 56. n = 4; **P < 0.01 (Wilcoxon rank sum).
