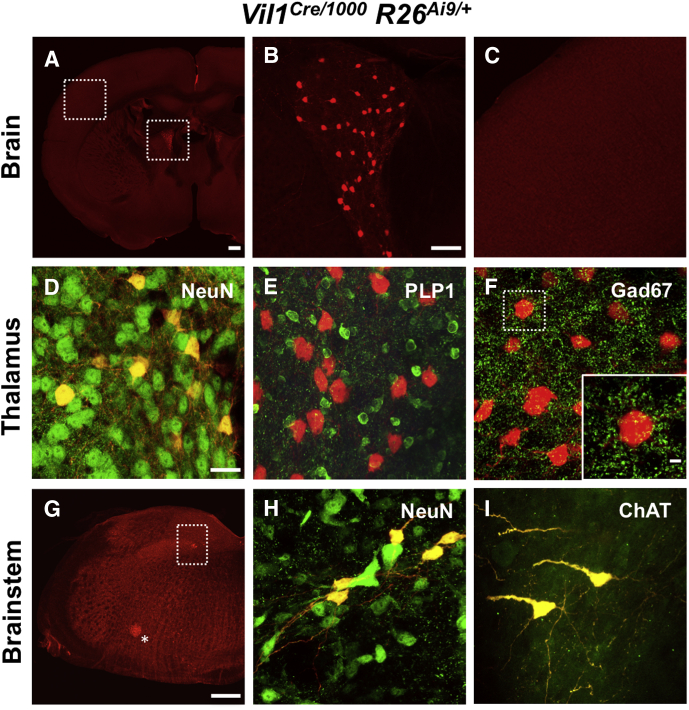
Figure 1.
The Vil1 promoter drives Cre recombinase expression in the CNS. (A–C) Coronal section from a Vil1Cre/1000 Rosa26Ai9/+ mouse brain shows TdTomato expression in cells within a periventricular region of the forebrain consistent with the anterodorsal thalamic nucleus (A and B) but not in the cerebral cortex (A and C). (D–F) Immunohistochemical staining of a Vil1Cre/1000 Rosa26Ai9/+ mouse brain shows that all TdTomato+ neurons within the anterodorsal thalamus (AD) co-localize with the pan-neuronal marker NeuN (D) but not the glial marker PLP1 (E). Thirty-eight percent ± 15% of NeuN+ neurons in the AD thalamus expressed TdTomato (mean ± standard deviation, n = 3 animals). TdTomato+ neurons are not immunoreactive for GAD67 but are contacted by many GAD67+ puncta, likely the terminals of GABAergic inhibitory neurons (F). (E) is from a mouse that was also hemizygous for the PLP1eGFP transgene. (G–I) Cross sections of brainstem from Vil1Cre/1000 Rosa26Ai9/+ mice show TdTomato expression in the dorsal and ventral medulla. All TdTomato+ cells co-localized with NeuN and ChAT, the biosynthetic enzyme for acetylcholine (shown in H and I for dorsal medulla and boxed region in G). TdTomato+ neurons in the dorsal medulla localized to the nucleus of the solitary tract (boxed region in G) and those in the ventral medulla to the nucleus ambiguus (asterisk in G). Scale bars for A and G = 400 μm; B and C = 75 μmol/L; D–F, H, and I = 25 μm.