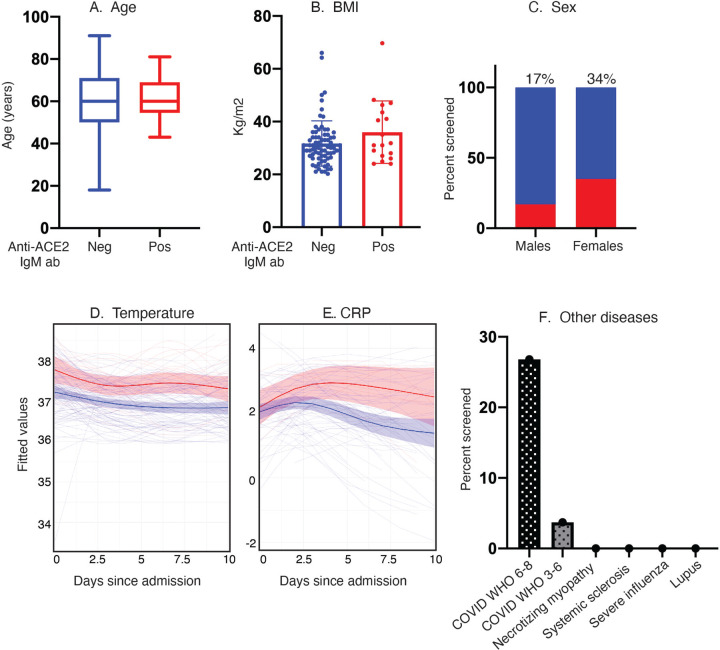
Figure 2: Clinical features of anti-ACE2 IgM-positive COVID-19 patients compared to those that do not have these antibodies.
A–E: Age, BMI, sex, temperature and CRP levels were compared between the anti-ACE2 IgM-positive and negative COVID patient groups. Red and blue colors denote anti-ACE2 IgM-antibody positive and negative status, respectively. Box plots show median, 25th and 75th percentiles, and whiskers min to max. Fig. 2D, E. IgM anti-ACE2 patients have higher average body temperature and CRP measurements beginning early after hospital admission. The IgM anti-ACE2-positive group had statistically significantly higher average temperatures and CRP levels over the first 10 days of hospitalization than the IgM-negative group (p = 0.0001 and 0.02, respectively). Analyses in both 2D and 2E use linear mixed-effects model Wald test with 4 degrees of freedom (see statistical methods. 2F: Anti-ACE2 IgM antibodies are detected in COVID-19 patients but not in other infectious and autoimmune disease controls.