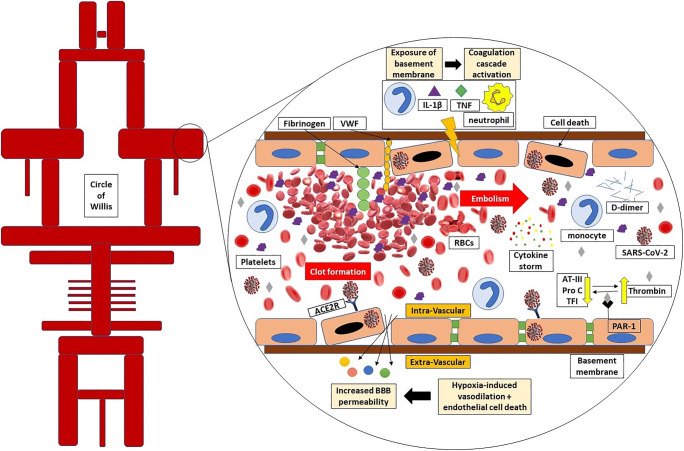
Fig. 2.
SARS-CoV-2 directly induces the endothelial cell death in the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The tight junctions in endothelial cells are destructed through monocytes, neutrophils, IL-1β, and TNF-α. In addition to underlying coagulopathy, the basement membrane and Von-Willebrand factor (VWF) contiguity with platelets and RBCs facilitate thrombus formation. The developed thrombus in the brain or other origins such as cardiac thrombus or deep vein thrombus can potentially embolize to distal parts or other branches. Hypoxia-induced vasodilation besides endothelial damage makes the possibility of SARS-CoV-2 dissemination to brain parenchyma or cerebrospinal fluid. High thrombin level due to low protein C, antithrombin III, and tissue factor pathway inhibitor amplifies the function of proteinase-activated inhibitor 1 (PAR-1) receptors which is led to inflammation. AT-III, antithrombin III; Pro C, protein c; TFI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor