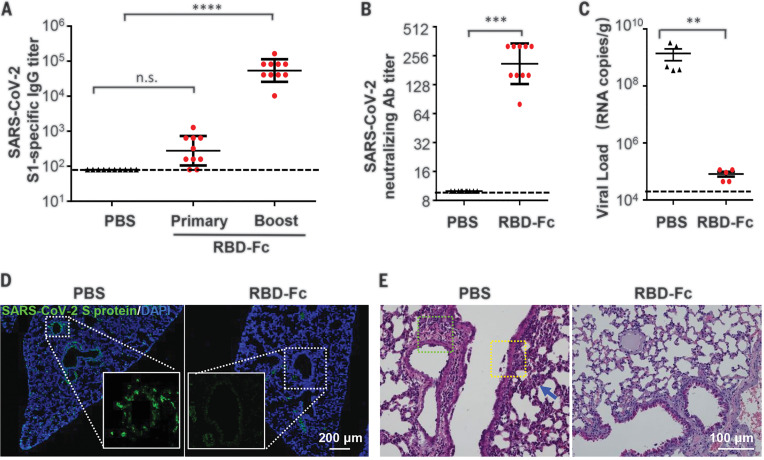
Fig. 4. Protection efficacy of the recombinant RBD-Fc vaccine candidate against MASCp6 challenge in mice.
(A) SARS-CoV-2–specific IgG antibody titers were detected with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay at 2 weeks after primary and boost immunization, respectively (n = 10 mice per group). Statistical significance was analyzed by means of one-way analysis of variance. (B) Neutralizing antibody titers against SARS-CoV-2 were determined with the microneutralization assay at 2 weeks after boost immunization (n = 10 mice per group). (C) Viral RNA loads in lung of vaccinated mice were detected at 5 days after MASCp6 challenge (n = 5 mice per group). Statistical significance was analyzed by means of Student’s t test. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of mouse lung sections for S protein (green) and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). The dotted boxes are magnified at the bottom of the same image. (E) H&E staining of mouse lung sections. Focal perivascular (green square) and peribronchiolar (yellow square) inflammation and thickened alveolar septa (blue arrow) are indicated. n.s., not significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.