Figure 5:
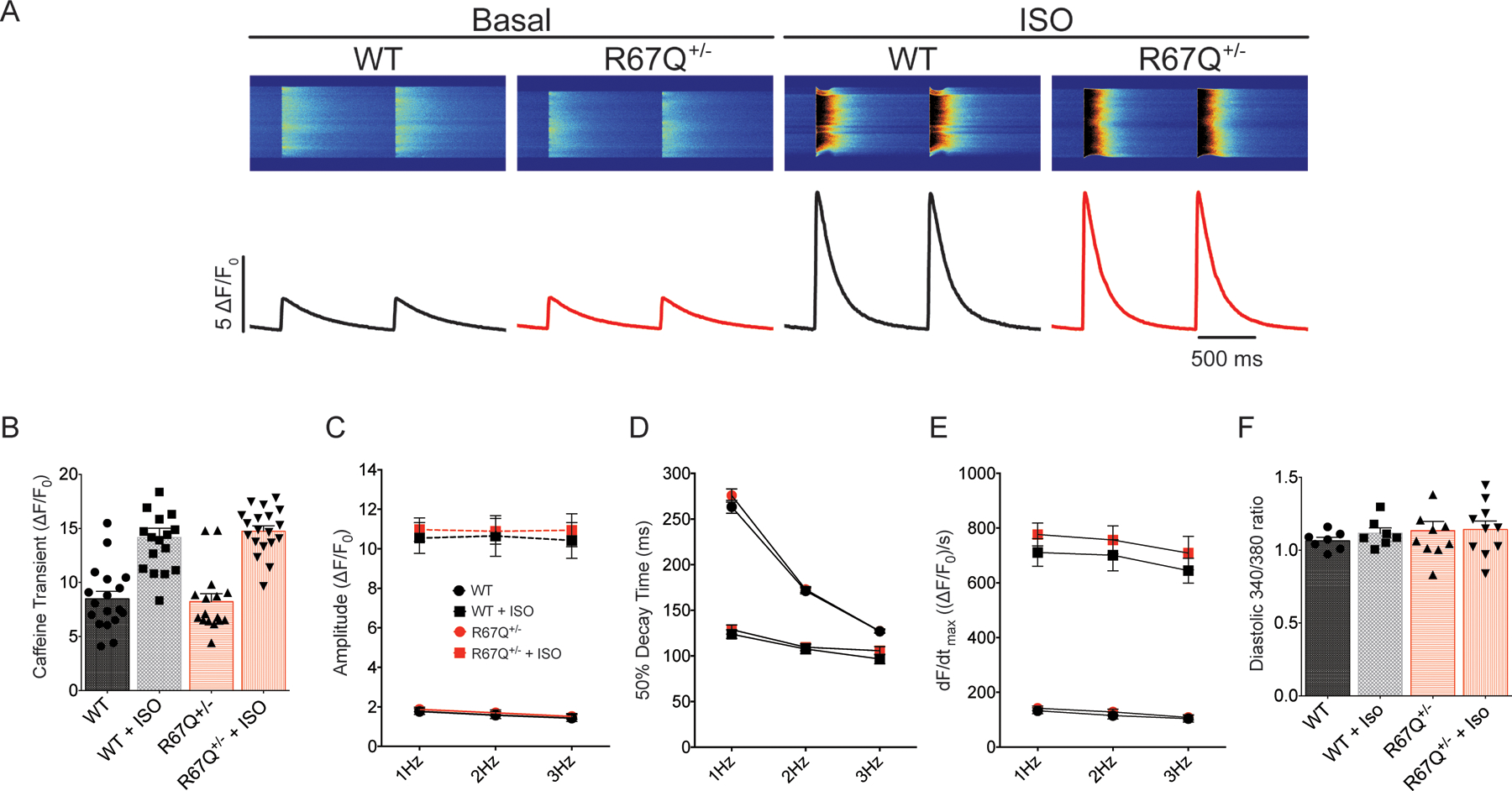
R67Q+/− does not impact Ca2+ handling. A. Representative calcium transient line-scans from WT and R67Q+/− myocytes. Cells were paced for 30s at 1Hz, 15s at 2Hz and 15s at 3Hz, followed by a pulse of 10 mM caffeine to measure SR content. B. WT and R67Q+/− myocytes had comparable SR calcium loads at baseline (8.48 ± 0.70 ΔF/F0 vs. 8.23 ± 0.73 ΔF/F0, respectively, p>0.1) and following treatment with ISO (14.17 ± 0.84 ΔF/F0 vs. 14.75 ± 0.49 ΔF/F0). (WT - N=4, n=18; R67Q+/− - N=4, n=16). C. No significant difference was observed in calcium transient amplitude between WT (black circles) and R67Q+/− (red circles) at baseline or following ISO (WT, black squares, R67Q+/−, red squares) (WT - N=4, n=18; R67Q+/− - N=4, n=16). D. 50% decay time was not significantly different between WT and R67Q+/− at baseline or following ISO. (WT - N=4, n=18; R67Q+/− - N=4, n=16). E. Velocity of the transient (dF/dtmax) is not significantly different between WT and R67Q+/− at baseline or following ISO. (WT - N=4, n=18; R67Q+/− - N=4, n=16). F. Ratiometric calcium transient measurements show no significant difference in diastolic calcium between WT and R67Q+/− VMs (p>0.05). (WT – N=6, n=7; R67Q+/− - N=4, n=10). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni correction was used (5B-F).
