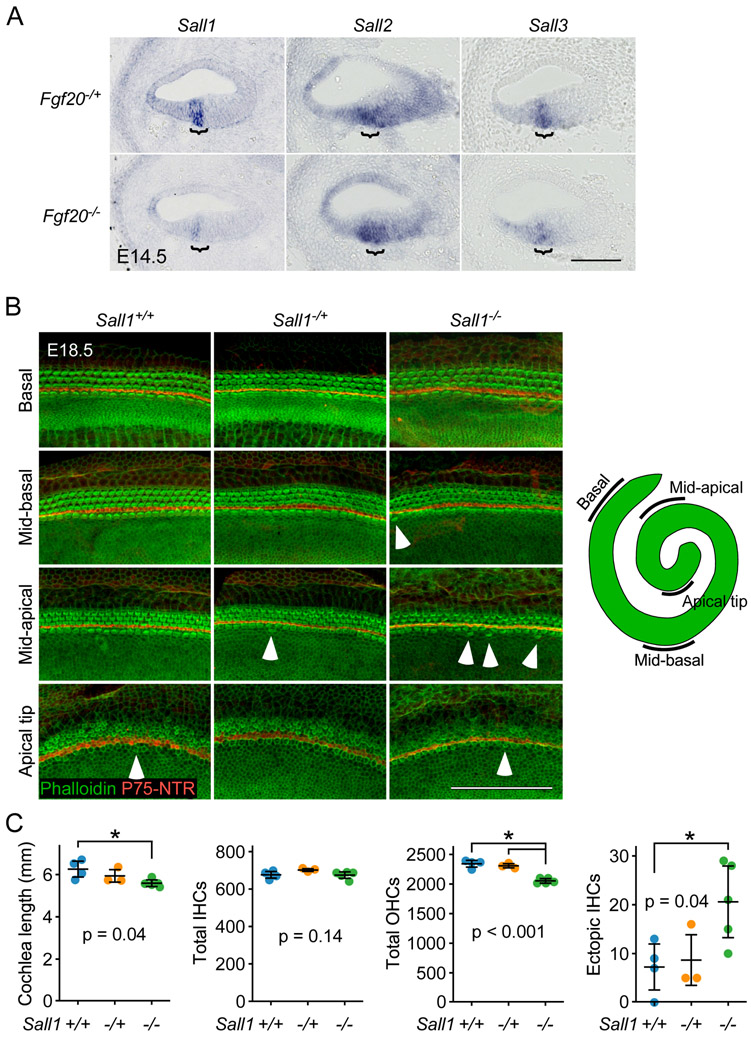
Figure 6. Sall1−/− cochleae exhibit an outer hair cell phenotype.
(A) RNA in situ hybridization for Sall1, Sall2, and Sall3 on sections through the middle turn of E14.5 Fgf20−/+ (Fgf20Cre/+) and Fgf20−/− (Fgf20Cre/βgal) cochlear ducts. Bracket, prosensory domain. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(B) Whole mount cochlea from E18.5 Sall1+/+, Sall1−/+, and Sall1−/− embryos showing inner hair cells and outer hair cells marked by phalloidin (green) and separated by inner pillar cells (p75NTR, red). Representative regions from the basal (5% of total length from the basal tip), mid-basal (33%), and mid-apical (67%) turns, and apical tip (90%) of the cochlea are shown. See schematic showing locations of the turns of the cochlea. Numerous ectopic inner hair cells were found throughout Sall1−/− cochleae, especially towards the apex (arrowheads). Scale bar, 100 μm.
(C) Quantification of cochlea length, total number of inner hair cells (IHCs) and outer hair cells (OHCs), and total number of ectopic IHCs in E18.5 Sall1+/+ (n = 4), Sall1−/+ (n = 3), and Sall1−/− (n = 5) cochleae. Error bars represent mean ± std. Results were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. P-values shown are from the ANOVA. * indicates p < 0.05 from Tukey’s HSD (ANOVA post-hoc).