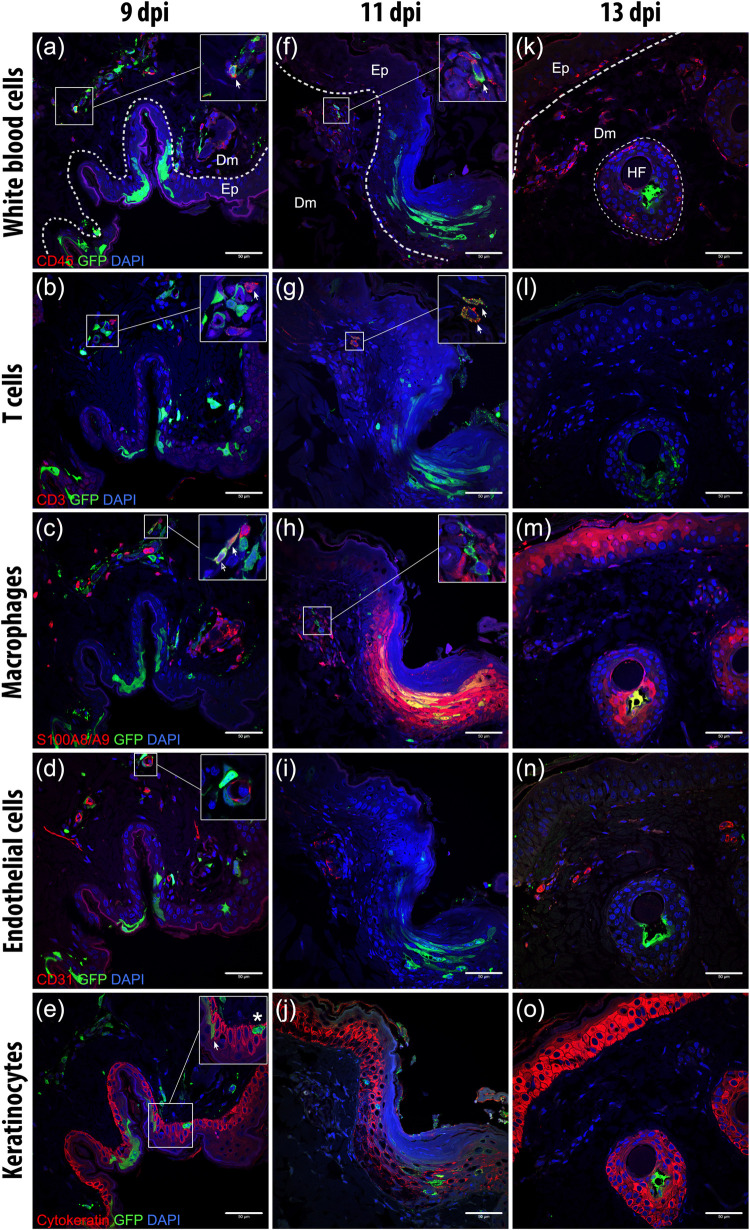
Fig 3. Phenotype of MV-infected cells in the dermis and epidermis throughout the course of infection.
Serial sections of skin (top to bottom) of three macaques (left to right) euthanized at three different time points (indicated at the top). The sections were double-stained with antibodies to EGFP (green) and several cell-specific markers (red), as indicated on the left of each row. Dashed lines indicate the basement membrane that separates the dermis (Dm) and the epidermis (Ep). MV-infected cells (green) could be observed in the dermis at 9 dpi. The progression of the infection in the same skin tissue at this time point differed between different sites: either MV-infected cells were found strictly in the dermis or the infection had spread to the epidermis. (a–e) Representative sequential images of MV infection that had progressed to the epidermis at 9 dpi. (a) MV-infected CD45+ leukocytes (inset, arrow) could be detected in the superficial dermis. (b) Some of these MV-infected leukocytes were CD3+ T cells, which were present in the dermis, mostly in reticular dermis, with speckled GFP signal in their cytoplasm (inset, arrow). (c) MV-infected S100A8/A9 complex+ (MAC387) macrophages (inset, arrow) were also found abundantly in the superficial dermis. (d) MV-infected cells in the dermis were often found in or around CD31+ blood vessels (inset). (e) In the epidermis, MV-infected cells were mostly keratinocytes (inset, arrow), although MV-infected non-keratinocyte cells (inset, asterisk) were observed in the basal epidermis. (f–j) Representative sequential images of MV infection at 11 dpi. (f) MV-infected leukocytes (inset, arrow), which were (g) T cells in the dermal papillae (inset, arrow), were in close proximity to (h) uninfected macrophages (inset) and (i) blood vessels. (j) The infection in keratinocytes had progressed apically and laterally. MV-infected keratinocytes and the surrounding uninfected keratinocytes expressed S100A8/A9 complex at this time point. (k–o) Representative sequential images of MV infection at 13 dpi. MV-infected cells had mostly disappeared from the dermis at 13 dpi. (k) The dermis and epidermis were filled with leukocytes. (l) No T cells could be observed in the dermal papillae. (m) Macrophages were present abundantly in this area. (n) At this time point, no MV-infected endothelial cells could be observed in the dermis despite their close proximity to (o) some MV-infected keratinocytes in the hair follicle (HF) area. Scale bar: 50 μm. Dpi: days post-inoculation.