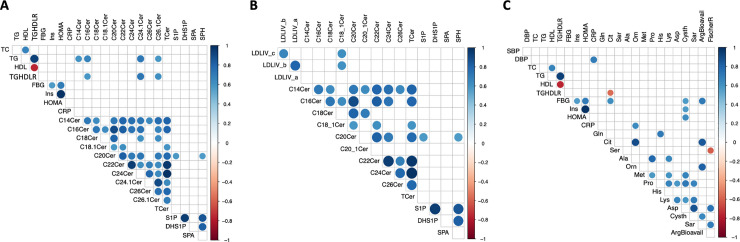
Fig 3.
Correlograms for specific changes in ceramides with A. Traditional biomarkers of cardiometabolic risk (CMR) and with B. Lipoprotein subspecies. The correlogram for amino acid metabolites with traditional CMR biomarkers is shown in C. Bivariate correlations between percent changes in ceramide and amino acid metabolites with percent changes in lipid and insulin resistance parameters were performed using pearson correlation analysis. Correlations with p values less than 0.01 are shown. Right colored bar indicates scale range of pearson correlation coefficients depicted. Dark red denotes negative, whereas blue indicates positive correlations observed. Arginine bioavailability ratio (ArgBioavail) was calculated using molar ratios of arginine and sum of citrulline and ornithine. Fischer ratio (FischerR) was calculated using the ratios of molar sum of branched chain amino acids (valine, leucine, and isoleucine and aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, and tyrosine). Abbreviations: SBP–systolic blood pressure, DBP–diastolic blood pressure, TC- total cholesterol; TG–triglyceride; LDL-low density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL–high density lipoprotein cholesterol; TGHDLR–TG to HDL-cholesterol ratio, FGB–fasting blood glucose, Ins–insulin, HOMA–homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; CRP–high sensitive C-reactive protein; LDL_IVb and IV_a (very small LDL); Cer—Ceramide, T. Cer—Total Ceramide, SPM—Sphinogomyelin, Gln—glutamine, Cit–citruilline, Ser–serine, Ala–alanine, Orn–ornithine, Met—Methionine, Pro–Proline, His–histidine, Cys–cysteine, Asp–aspartic acid, Cysth—cystathionine, Sar–sarcosine, DHSIP-Dihydrosphingosine-1-phosphate, SIP—Sphingosine-1-phosphate.