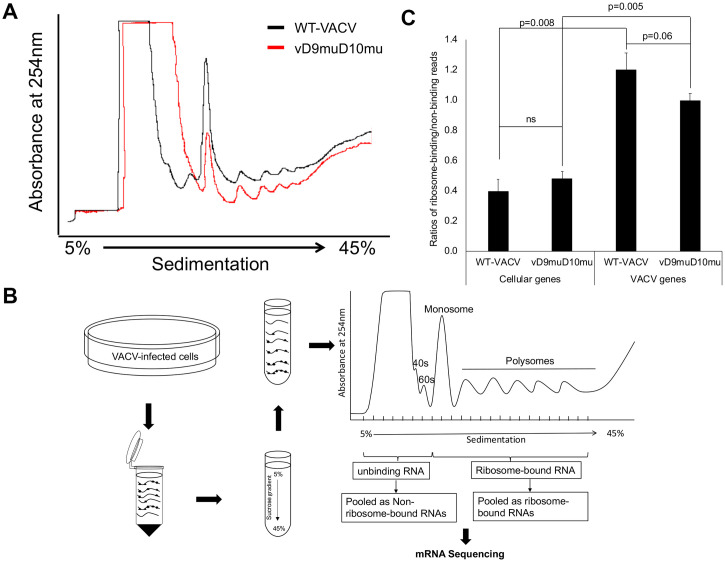
Fig 1. Inactivation of VACV decapping enzymes decreases overall translation activity in VACV-infected cells independent of PKR- and RNase L-mediated translational repression.
(A) Polysome profiling to compare translation activities in WT- and vD9muD10mu-infected A549DKO cells. Cell lysates from virus-infected A549DKO cells at 8 hpi were applied to the sucrose gradient and fractionated using a fractionator. The decreasing trend in vD9muD10mu-infected A549DKO cells was reproducible with three biological replicates. (B) Experimental design of ribosome-binding/non-ribosome-binding RNA-Seq. (C) Global cellular mRNA translation activities in WT and vD9muD10mu-infected cells. The ratios of read counts of ribosome-binding RNAs to non-ribosome RNAs for cellular genes and viral genes in WT and D9muD10mu-infected cells were analyzed. Three biological repeats were carried out. P values are shown.