Figure 1.
Uclacyanins UCC1 and UCC2 Are Required for a Functional Casparian Strip
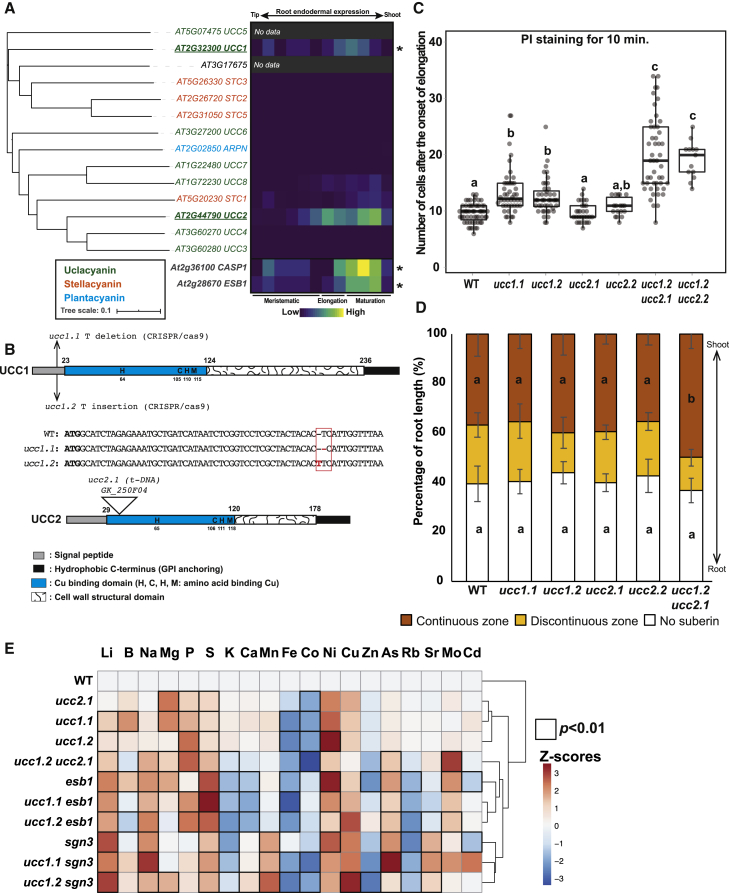
(A) Left: figure shows a phylogenetic analysis of phytocyanins protein family in A. thaliana. The tree was built using the full-length amino acid sequences for all proteins. Different colors represent the three phytocyanins subfamilies: uclacyanins, stellacyanins, and plantacyanins (39). In the tree, branch lengths are proportional to the number of substitutions per site. AT3G17675 has been previously annotated as a stellacyanin (STC4), however, the signal peptide for the secretion pathway and the hydrophobic extension for Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchoring are missing. Right: heatmap showing the endodermal expression of the phytocyanins family in A. thaliana across the different root zones (Meristematic, Elongation, Maturation). For the analysis, expression data were collected from the Bio-Analytic Resource database, AtGenExpress Consortium. The expression of two endodermal localized proteins, CASP1 and ESB1, were added to the analysis as a reference. Asterisks indicate a significant downregulation in a myb36 mutant according to [18].
(B) Schematic representation of the UCC1 and UCC2 proteins showing the different protein domains and the types of mutations. Domains were defined according to [19] (see also Figure S1A).
(C) Boxplot analysis showing the number of the cells from the onset of elongation permeable to propidium iodide in wild-type (WT) plants, ucc1 mutants (ucc1.1 and ucc1.2), ucc2 mutant (ucc2.1 and ucc2.2), and the double ucc1 ucc2 mutants (ucc1.2 ucc2.1 and ucc1.2ucc2.2). Data were collected from two independent experiments (n ≥ 29). Different letters represent significant statistical differences between genotypes using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test (p < 0.01) (see also Figure S1B).
(D) Diagram shows the quantification analysis of the endodermal suberization in roots of WT plants, ucc1.1, ucc1.2, ucc2.1, ucc2.2 and ucc1.2 ucc2.1. Each color in the graph represents the percentage of the root length (percentage of root length [%]) that is unsuberized (white), discontinuously suberized (yellow), continuously suberized (orange). Suberin was staining with Fluorol yellow 088. (n ≥ 18). Error bars in the figure are the standard deviation (SD). Different letters represent significant differences between genotypes using a Mann-Whitney test (p < 0.01) (See also Figure S1C).
(E) Heatmap representing the ionomic profiles (Z-scores) of WT plants, and a collection of mutants with a defective Casparian strip: ucc2.1, ucc1.1, ucc1.2, ucc1.2 ucc2.1, esb1, ucc1.1 esb1, ucc1.2 esb1, sgn3, ucc1.1 sgn3, and ucc1.2 sgn3 grown in full nutrient conditions on agar plate for 2 weeks (n = 10). Elements concentration were determined by ICP-MS and the raw data are available in the Table S1. Significant differences were determined in comparison with WT using a t test (p < 0.01). Genotypes were subjected to hierarchical clustering analysis.