Figure 2.
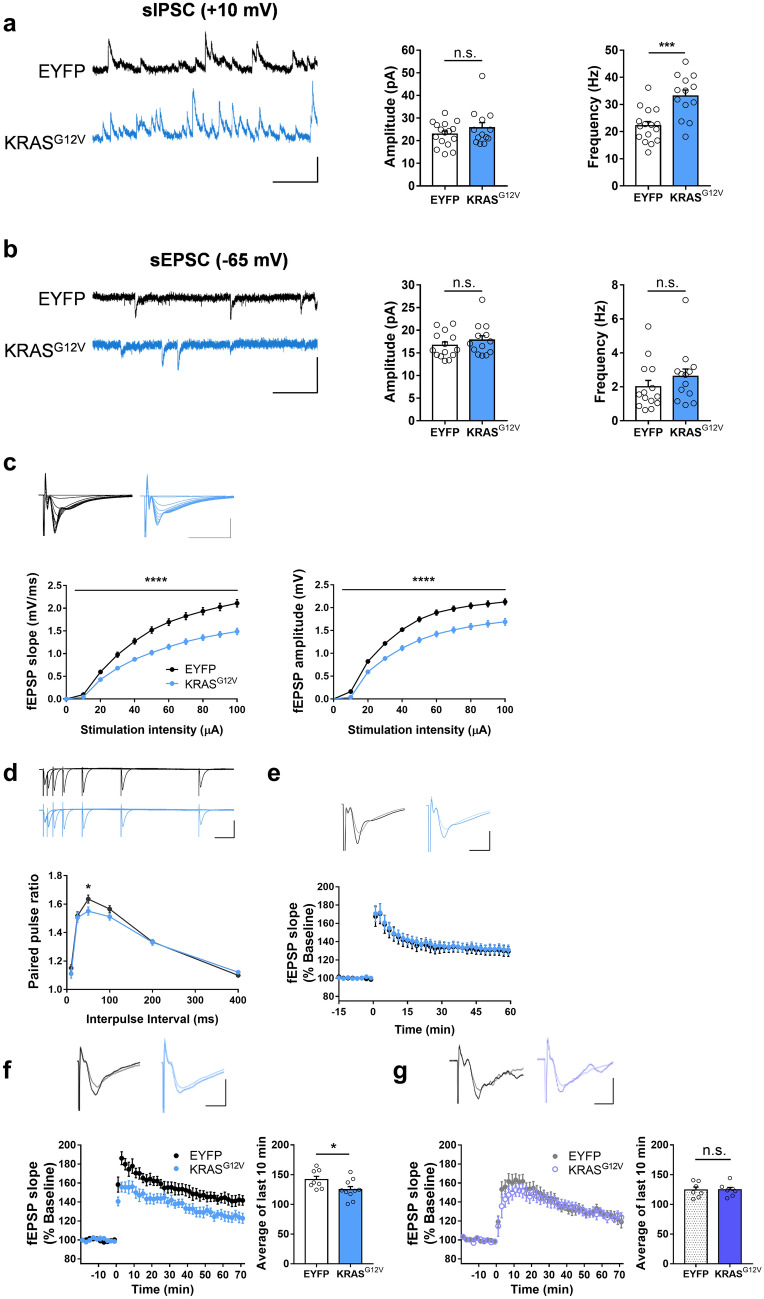
Ectopic KRASG12V expression in the inhibitory neurons increases inhibitory synaptic transmission and impairs LTP. (a) Ectopic KRASG12V expression in the inhibitory neurons increased the frequency of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic current (sIPSC). The amplitudes of the sIPSCs in the vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V mice were comparable to that from vGAT- Cre::EYFP mice (EYFP, n = 16 cells from 3 mice; KRASG12V, n = 13 cells from 3 mice, unpaired t-test, P = 0.2883). The frequencies of the sIPSCs in the vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V mice were higher than that in the vGAT-Cre::EYFP mice (EYFP, n = 16 cells from 3 mice; KRASG12V, n = 13 cells from 3 mice, unpaired t-test, ***P = 0.0003). Vertical bar, 50 pA; horizontal bar, 200 ms. (b) Ectopic expression of KRASG12V in the inhibitory neurons did not affect either the frequency or the amplitude of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current (sEPSC). The amplitudes of the sEPSCs were comparable between vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V and vGAT- Cre::EYFP; (EYFP, n = 14 cells from 3 mice; KRASG12V, n = 13 cells from 3 mice, unpaired t-test, P = 0.3528). The frequency of the sEPSCs from the vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V were similar with that from vGAT-Cre::EYFP; KRASG12V (EYFP, n = 14 cells from 3 mice; KRASG12V, n = 13 cells from 3 mice, unpaired t-test, P = 0.3044). Vertical bar, 50 pA; horizontal bar, 200 ms. (c) Ectopic KRASG12V expression in the inhibitory neurons significantly decreased the input–output relationship of the field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) at CA3-CA1 synapse. Outputs were measured either by initial fEPSP slope (left) or peak amplitude (right). vGAT-Cre::EYFP, n = 20 slices from 10 mice; vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V, n = 23 slices from 10 mice; Two-way repeated measures ANOVA, effect of virus, ****P < 0.0001 for both slope and amplitude. Vertical bar, 1 mV; horizontal bar, 10 ms. (d) Paired pulse facilitation ratio was significantly decreased at 50 ms interpulse interval in vGAT-Cre::KRASG12Vmice. vGAT-Cre::EYFP, n = 20 slices from 10 mice; vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V, n = 23 slices from 10 mice, unpaired t-test, *P = 0.0403. Vertical bar, 1 mV; horizontal bar, 50 ms. (e) Ectopic KRASG12V expression in inhibitory neurons did not affect long-term potentiation (LTP) induced by weak stimulation protocol (4 bursts of 4 100 Hz pulses, 5 Hz inter-burst interval). vGAT-Cre::EYFP, n = 10 slices from 5 mice; vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V, n = 12 slices from 5 mice. Traces represent the average of fEPSPs at the baseline (-15 min – 0 min) and after LTP induction (50 – 60 min). Vertical bar, 1 mV; horizontal bar, 5 ms. (f) Ectopic KRASG12V expression in inhibitory neurons significantly impaired LTP induced by the stronger stimulation protocol (10 bursts of 4 100 Hz pulses, repeated 4 times with 10 s interval). vGAT-Cre::EYFP, n = 8 slices from 5 mice; vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V, n = 10 slices from 5 mice. The averages fEPSP slope of 61 to 70 min after LTP induction were compared. Unpaired t test, *P = 0.0422. Traces represent the average of fEPSPs at the baseline (-20 min – 0 min) and after LTP induction (61 – 70 min). Vertical bar, 1 mV; horizontal bar, 5 ms. (g) Picrotoxin (10 μM) treatment rescued the strong TBS-induced LTP deficit at CA3-CA1 synapse in vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V mice. vGAT-Cre::EYFP, n = 7 slices from 3 mice; vGAT-Cre::KRASG12V, n = 7 slices from 3 mice. The averages fEPSP slope of 61 to 70 min after LTP induction were compared. Unpaired t test, P = 0.9887. Traces represent the average of fEPSPs at the baseline (-20 min – 0 min) and after LTP induction (61 – 70 min). Vertical bar, 1 mV; horizontal bar, 5 ms. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM.