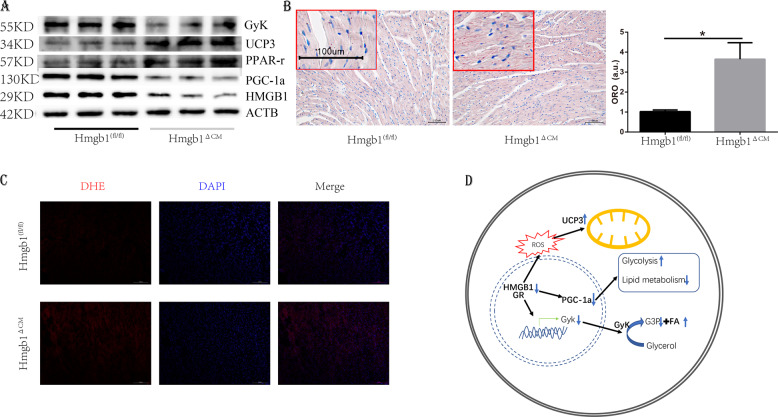
Fig. 6. Deletion of HMGB1 in cardiomyocytes decreases PGC-1α signalling.
a Western blot analysis and quantification of PGC-1α, PPAR-γ, UCP3 and GyK levels in control and HMGB1△CM ventricles at 12 weeks (n = 6). b Representative heart Oil red O staining and quantification of control and HMGB1△CM mice at 12 weeks, n = 6/group, bar = 100 μm. Insets from the images are magnified four times in order to highlight the lipid staining. Bar charts showing the percentage of cardiomyocytes that are oil red staining, a.u. arbitrary units, *p < 0.05 versus control, t-test, mean ± SEM. c Detection of superoxide by DHE staining at 12 weeks, bar = 100 μm, n = 4/group. d Model of the signalling mechanism: HMGB1 inhibits GR activity, further inactivates PGC-1α and GyK, causes increased glycolysis, and decreases lipid metabolism.