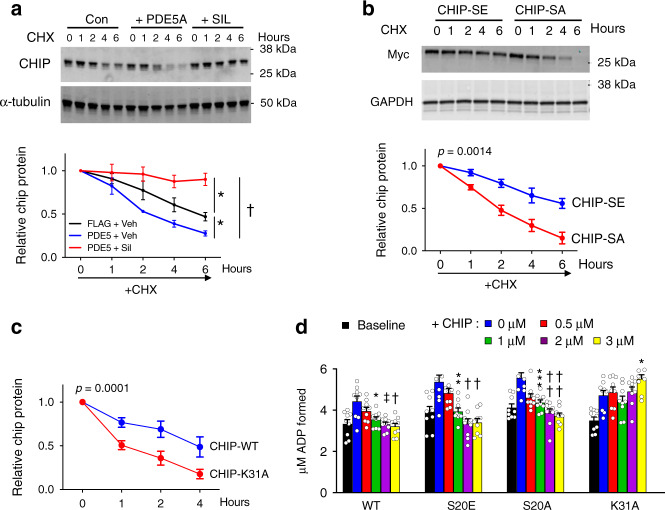
Fig. 7. Influence of S20 modification on CHIP post-translational half-life.
a NRCMs infected with AdV-Flag or AdV-Flag-PDE5 to reduce PKG activation, and with SIL added to enhance PKG activation placed in media containing cycloheximide (CHX, 100 µM) to block protein synthesis and H2O2 (50 µM) to induce oxidative stress. N = 4–5 separate experiments with 5 independent time points per experiment. ANCOVA results for differences between paired relations: *p = 0.001; †0.000009. b Same general protocol but with NRCMs over-expressing either S20A or S20E CHIP mutants. P-value for slope difference by ANCOVA. c Same protocol but WT and K31A CHIP mutants. P-value for offset difference by ANCOVA. d Hsp70/Hsp40 dependent protein refolding ATPase assay showing capacity of CHIP to reduce activity in a dose dependent manner in wild type (WT), S20A, and S20E CHIP mutants. K31A CHIP expression prevents this negative modulation. N = 9 biological replicants, RMANOVA performed within each experiment, Dunnets mct: *p = 0.004; **0.006, ***0.002; †0.0005, ††0.0002, ‡p = 0.002 – each versus no CHIP added (blue bar). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Regressions (a–c) and summary plot (d) each display mean ± SEM.