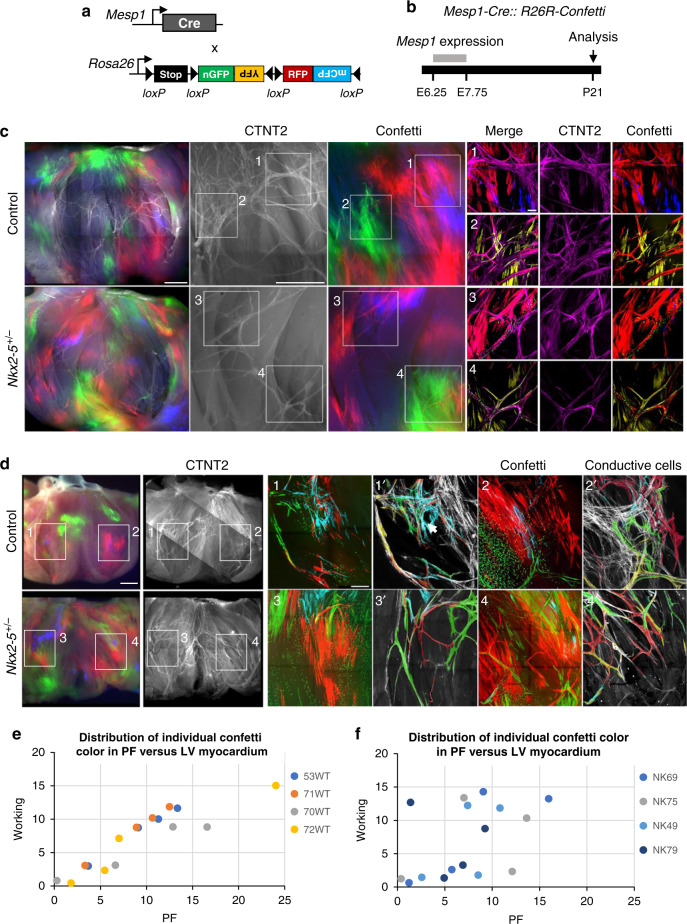
Fig. 4. Mosaic tracing analysis of Mesp1+ early cardiac progenitors.
a Scheme illustrating the genetic tracing strategy using R26R-Confetti multicolor reporter mouse line crossed with non-inducible Mesp1-Cre mice. b Recombination of the confetti allele occurs during the short time-window of Mesp1 expression, between E6.25 and E7.75. Mosaic tracing analysis in control and Nkx2-5+/− mice is performed at P21. c Whole-mount fluorescence views of Mesp1-Cre::R26R-Confetti opened-left ventricles at P21. Immunostaining for Contactin-2 (CNTN2) is used to label the mature PF network. Small panels (1–4) show high magnification confocal images of different PF network regions. Scale bars = 1 mm and 100 µm in insets. d Small panels (1–4) show high magnification confocal images of the PF network. Panels (1′–4′) are image reconstructions in which conductive only confetti+ cells are manually drawn. Non-conductive confetti+ cells are not represented. In control hearts, conductive confetti+ cells form either small or large monochromatic clusters. Large clusters (arrows) contribute to complex parts of the PF network. In Nkx2-5+/− hearts, only small clusters contribute to the hypoplastic network. Scale bars = 1 mm and 200 µm in insets. e and f Dot plots of individual Mesp1+ confetti colors showing percentage contribution to the working myocardium versus PF network in control (WT) or Nkx2-5+/− (NK) hearts.