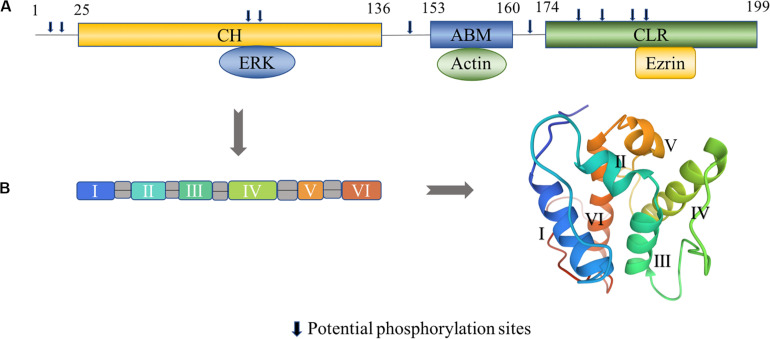
FIGURE 1.
Structural characteristics of transgelin. (A) Human transgelin consists of three regions: an N-terminal calponin-homolog (CH)-domain, an actin-binding motif (ABM), and a C-terminal calponin-like repeated (CLR)-region. The CH domain binds to ERK, the ABM domain binds to actin, and the C-terminal CLR domain binds to ezrin (Yin et al., 2019). Potential phosphorylation sites amino acids number 8, 11, 83, 84, 145, 163, 180, 185, 190, and 192 in T-2. (B) The tertiary fold of the CH domain (PDB: 1H67). The CH domain contains six α-helices, in which two short helical structures (II and V) and a core of four α-helices (I, III, IV, and VI) are present. Helices III and VI are approximately parallel, while helix IV is lying oblique to the other helices (Yin et al., 2020). The 3D view of the structural model was generated from the data file from the Protein Data Bank.