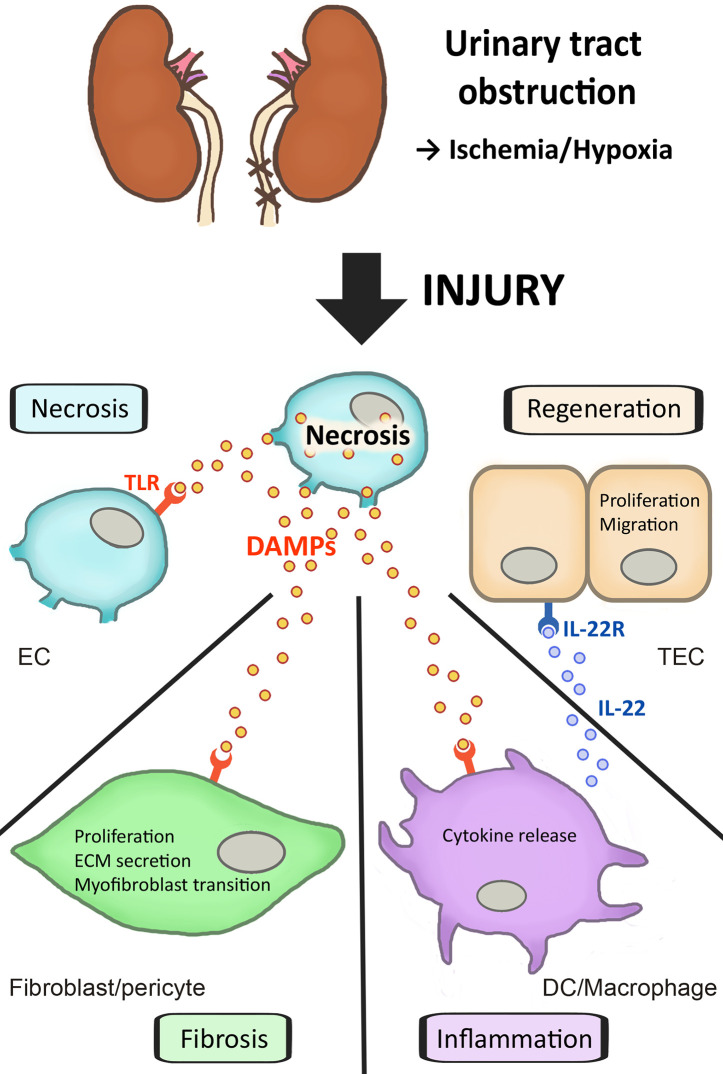
Figure 2.
Different outcomes of cell death and DAMP release due to urinary tract obstruction. Unilateral ureteral obstruction causes cell injury and necrosis, as well as the regulated forms necroptosis and pyroptosis. Due to cell stress and cell death DAMPs are released by injured endothelial (EC) and tubular epithelial (TEC) cells. These DAMPs activate PRRs such as TLRs on other cells. This can lead to further renal cell necrosis, with amplification of DAMPs. Fibroblasts and pericytes activated by DAMPs trigger fibrosis through proliferation, ECM secretion and myofibroblast transition. Activated dendritic cells (DC) and macrophages release cytokines and chemokines, which initiate an inflammatory response. IL-22 secreted by renal DCs, on the other hand, is able to activate the IL-22 receptor on TECs, which accelerates tubular re-epithelialization, thus promoting regeneration of TECs.