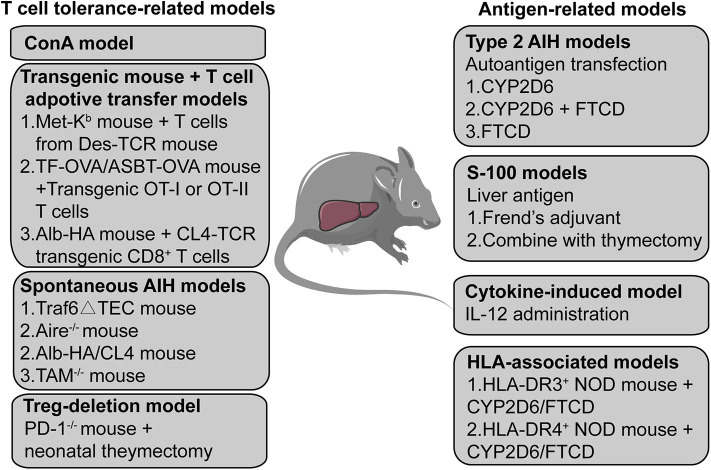
Figure 2.
A summary of AIH mouse models. The mouse models are divided into two categories; one is based on a T cell-related mechanism and the other is based on an autoantigen- or liver antigen-related mechanism. The ConA mouse model is the most widely used mouse model to investigate acute T cell-mediated liver injury. Transgenic mice combined with T cell adoptive transfer also provides a method to establish an AIH mouse model. Some transgenic or gene knockout mice can develop spontaneous AIH-like disease. Treg depletion may also function as a potential method to induce AIH in mice. Transfecting the human autoantigen CYP2D6 or FTCD from type 2 AIH into mice may simulate the initiation process of type 2 AIH in humans to establish a chronic type 2 AIH mouse model. S-100, a supernatant of syngeneic liver homogenate, has also been used to induce AIH in mice. The expression of transgenic IL-2 in hepatocytes causes loss of tolerance of hepatocellular antigens, leading to chronic type 1 AIH-like disease in mice. Transfection HLA-DR3 or HLA-DR4 transgenic mice with the non-obese -diabetic background with a plasmid containing CYP2D6 and FTCD can also induce AIH.