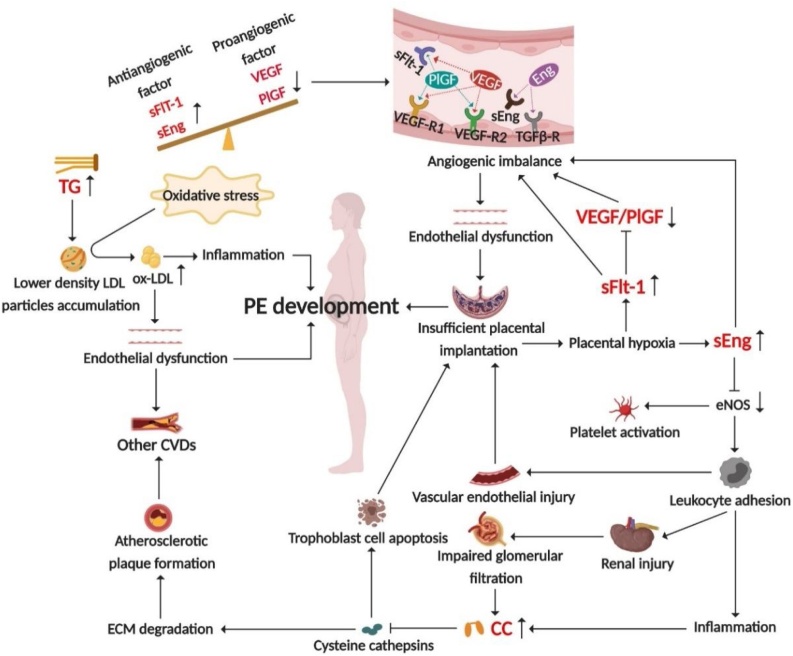
Fig. 6.
The vascular endothelial injury hypothesis illustrating the pathogenesis of PE.
The expression of antiangiogenic factors such as sFlt-1 and sEng increased in PE patients, while the expression of proangiogenic factors such as VEGF decreased, which is manifested as an imbalance of angiogenesis and extensive endothelial injury, resulting in insufficient placental implantation, impaired glomerular filtration, and increased CC level. TG levels in PE patients also elevated, and they were prone to form ox-LDL under oxidative stress, leading to endothelial dysfunction and systemic inflammation, and participating in the pathogenesis of PE.