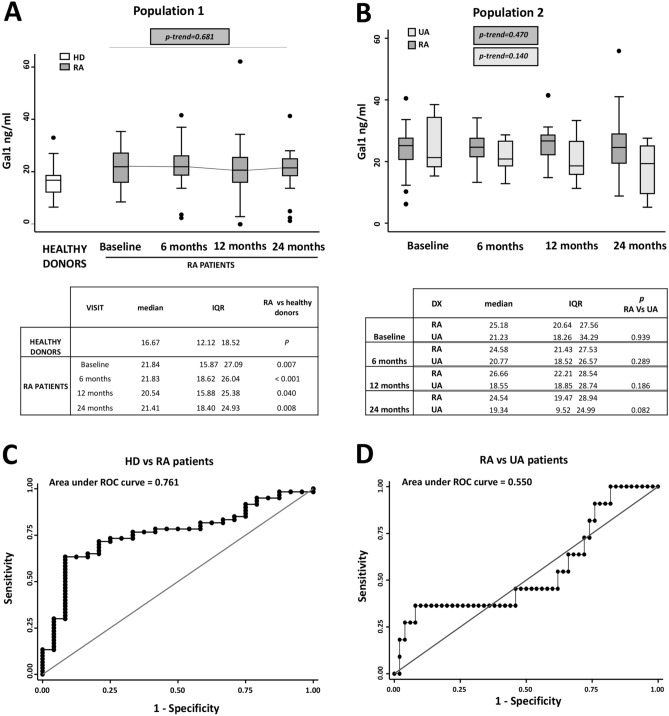
Figure 1.
Gal1 serum levels are increased in early arthritis patients compared with healthy donors. (A) Determination of Gal1 serum levels by ELISA in healthy donors (HD) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients from PEARL study (Population 1). (B) Determination of Gal1 serum levels by ELISA in early arthritis patients (undifferentiated arthritis [UA] and RA) from PEARL study (Population 2). Data are shown as interquartile range (p75 upper edge of box, p25 lower edge, p50 midline) as well as the p95 (line above box) and p5 (line below). Dots represent outliers. Statistical significance for the trend of Gal1 across the visits in patients was determined with the Cuzick’s non-parametric test. Significance threshold was set at p-trend < 0.05. Tables below the panels show the statistical significance between HD and each visit of RA patients (A) or between RA and UA patients in each visit (B). Statistical significance was determined with Mann–Whitney test. Significance threshold was set at p < 0.012 due to multiple comparisons, according to Bonferroni correction. (C) ROC curve analysis to assess Gal1 capacity to discriminate between RA patients and healthy donors. (D) ROC curve analysis to assess Gal1 capacity to discriminate between RA patients and UA patients.