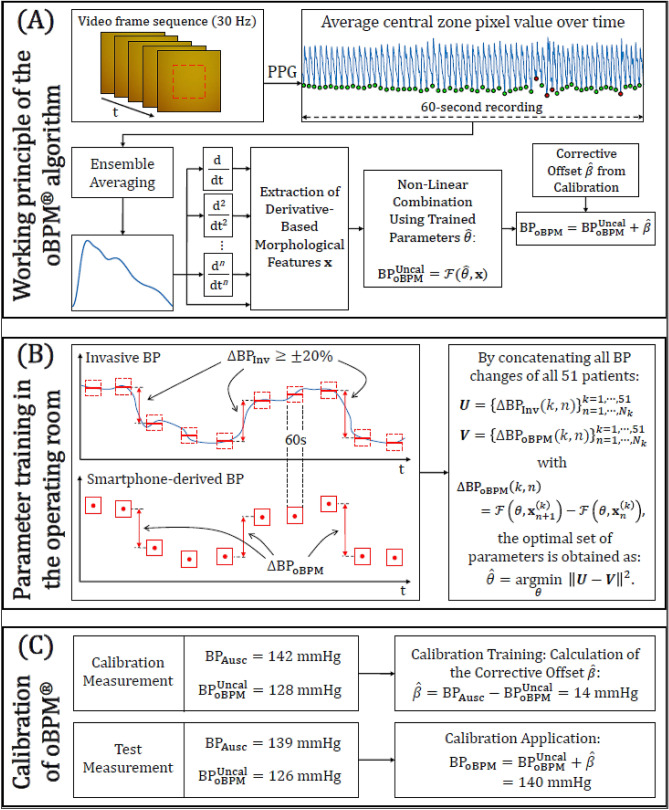
Figure 2.
Algorithm description, parameter training, and calibration. (A) Working principle of the oBPM (optical blood pressure monitoring) algorithm. The oBPM algorithm automatically identifies all individual pulses in the PPG signal and ensemble averages them. Pulses with un-physiological morphologies (red dots) are identified and assigned low weights in the ensemble averaging procedure, whereas the remaining pulses (green dots) are assigned a stronger influence. The resulting ensemble average waveform is fed to a filter bank of time-derivative filters, allowing a decomposition of the waveform at various time resolutions. From their outputs, a set of features characterizing the morphology of the waveform is obtained and nonlinearly combined using a pre-trained set of parameters (see (B) panel of the figure). The result is an uncalibrated BP value, . The final oBPM-derived BP estimate () is obtained after application of the previously trained corrective calibration offset . (B) Training of the parameters of the oBPM algorithm. The parameters were trained using the data acquired in the operating room. Significant BP changes () between successive recordings were identified in the arterial line measurements. Their corresponding oBPM-derived BP changes () were then calculated to be compared. The set of oBPM parameters was optimized by minimizing the cohort-wise error between and in the least-square sense. In the figure, is the number of significant BP changes found for patient , and is the non-linear oBPM model mapping the features to BP values using the parameters . (C) Illustration of the calibration procedure. The calibration consists in the addition of a per-patient corrective offset to the uncalibrated oBPM-derived BP estimate for systolic, diastolic and mean BP individually. It is illustrated here with numerical values for ease of understanding. During the calibration measurement, the corrective offset is calculated. Applying the calibration to the following test measurements consists of the addition of to the uncalibrated BP estimate outputted by oBPM.