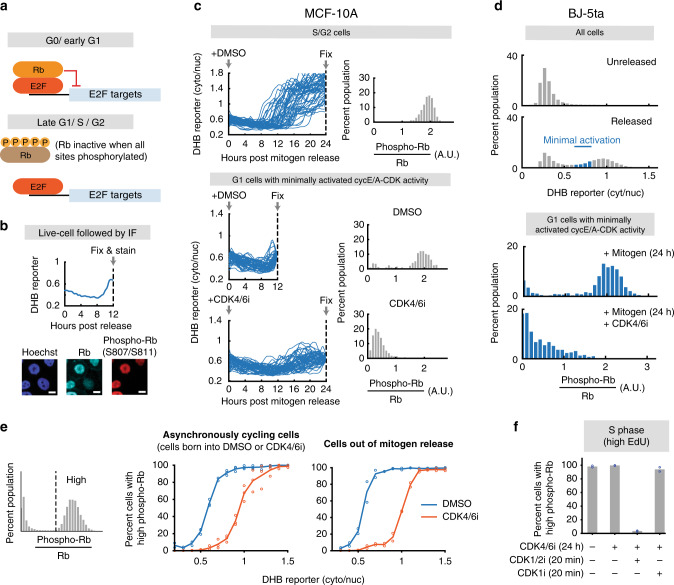
Fig. 3. Cyclin E-CDK2 is activated without Rb hyperphosphorylation in cells lacking CDK4/6 activity.
a E2F is active when Rb is hyperphosphorylated. b Phospho-Rb analysis after live-cell tracking of cyclin E/A-CDK activity. Scale bar = 10 µm. c Phospho-Rb(S807/S811) analysis of cells that have inactivated APC/CCDH1 (top; 50 cells plotted, 2315 cells total), and cells that have initiated cyclin E/A-CDK activity and have not inactivated APC/CCDH1 (bottom; 50 cells plotted, 364, 1023 cells for DMSO and CDK4/6 inhibitor). One of n = 3 biological replicates. d BJ-5ta cells expressing the cyclin E/A-CDK activity reporter and APC/C degron reporter were mitogen released with or without 1 µM CDK4/6 inhibitor, fixed after 24 h, and stained for Rb and phospho-Rb(S807/S811). G1 cells with recently activated cyclin E/A-CDK activity were analyzed. n = 703 and 383 cells for DMSO and CDK4/6i condition. e Cells were grouped into high and low phospho-Rb(S807/S811) signal populations. The percentages of cells with high signal were then determined for each bin of the cyclin E/A-CDK activity. Middle: Cells born into DMSO or CDK4/6 inhibitor. Mean of n = 3 biological replicates. Right: Cells mitogen released with DMSO or CDK4/6 inhibitor. Mean of n = 2 biological replicates. f Asynchronously cycling cells treated with or without CDK4/6 inhibitor for 24 h. Cells were then incubated with 10 µM EdU for 15 min, and then treated with DMSO, CDK1/2i (3 µM), or CDK1i (10 µM) for 20 min. Cells were then fixed and high EdU signal cells were examined. Mean of n = 2 biological replicates.