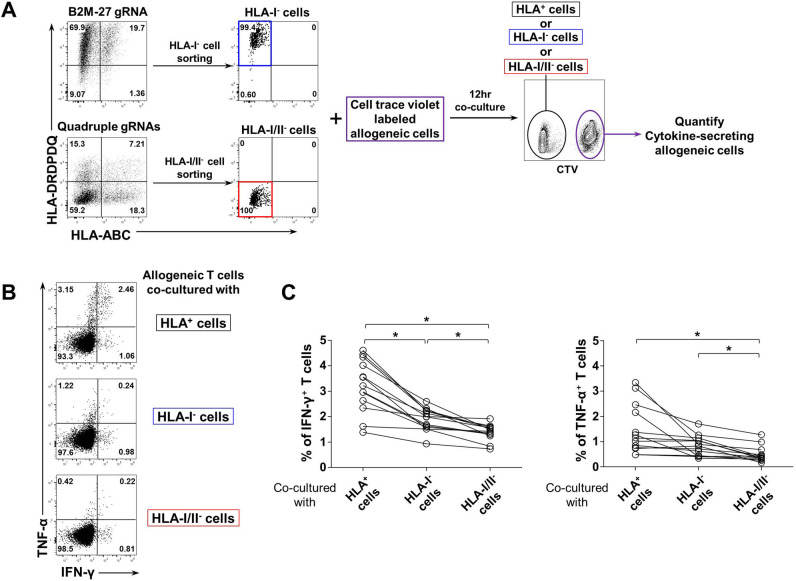
Figure 4.
HLA-II ablation in HLA-I-negative T cells further reduces allogeneic T cell activation. (A) A schematic diagram of experimental design for (B,C) Human primary CD3+ T cells isolated from healthy donor PBMC were transfected with non-targeting gRNA (control gRNA), B2M gRNA (B2M-27 gRNA), or a mixture of quadruple gRNAs each targeting B2M, HLA-DRA, HLA-DQA and HLA-DPA (quadruple gRNAs) together with Cas9 protein and expanded ex vivo. On day 14, the expanded T cells were sorted according to their HLA expression and γ-irradiated. Another set of allogeneic human PBMCs stained with CTV was co-cultured with the sorted T cells for 12-h. (B) A representative flow cytometry plot depicting the numbers of cytokine-producing allogeneic CTV+ CD3+ T cells co-cultured with the HLA+ (top), HLA-I− (middle), or HLA-I/II− T cells (bottom), respectively. (C) Quantification of IFN-γ (left) or TNF-α-secreting (right) cells among the total allogeneic CD3+ T cells from (B) are presented. Each dot represents different alloreactive donor (n = 13). Pooled results from 4 independently performed experiments are shown. *p < 0.05, by Friedman test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test.