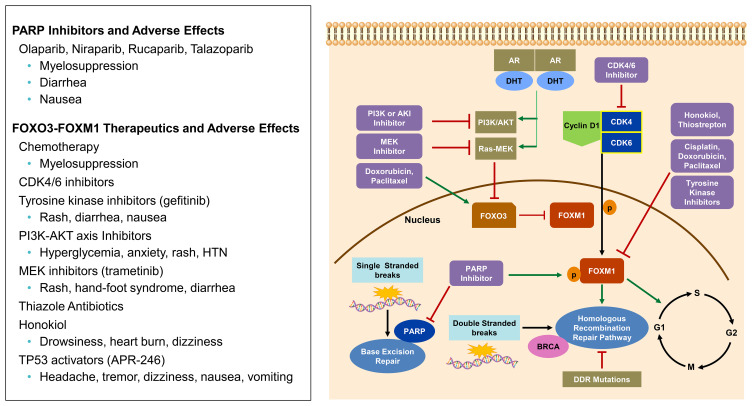
Figure 2.
CDK4/6 pathway and FOXO3-FOXM1 axis: Cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex phosphorylates FOXM1 transcription factor which is involved in expression of G1/S phase genes. FOXM1 also up-regulates genes involved in the homologous recombination Repair (HRR) pathway. FOXO3, when acting as a tumor suppressor gene, inactivates FOXM1. The tumor suppressor activity is regulated by PI3K/AKT and Ras-MEK. Multiple therapeutics have been shown to have activity in the FOXO3-FOXM1 axis. PARP inhibitors can increase FOXM1 expression and nuclear localization. PARP is involved with base excision repair (BER), however, if PARP is inhibited single stranded breaks accumulate and double stranded breaks occur making the cell rely on HRR. If HRR is deficient, by mutation (i.e BRCA), then synthetic lethality occurs in the presence of PARP inhibition.