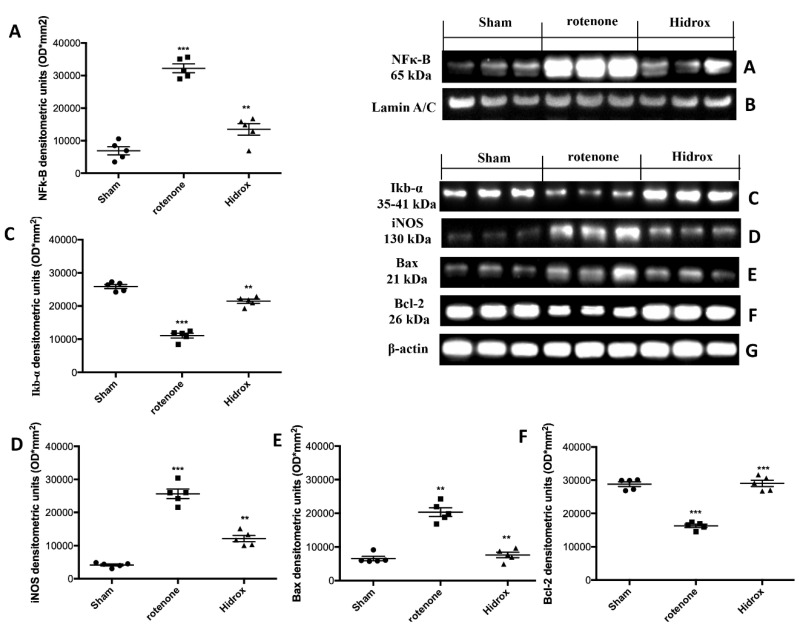
Figure 8.
Effects of HD on expression of IκB-α and nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 and on iNOS after rotenone intoxication. NF-kB levels were significantly increased in the nuclear fraction compared to the Sham animals (A). HD treatment significantly reduced NF-kB translocation (A). Basal levels of IkB-α were found tissues from Sham group; they were notably reduced in samples from the rotenone-treated mice (C). HD administration significantly reduced IkB-α degradation (C). Western blot analysis of tissue lysates from rotenone-treated mice shows significant increases in iNOS expression after 28 days. HD significantly lowered the expression of iNOS in the SN after rotenone intoxication (D). Western blot analysis demonstrated Bad expression to be significantly increased in the rotenone group, whereas treatment with HD significantly limited the rise in Bad expression (E). Finally, Bcl-2 expression was reduced after rotenone intoxication; however, treatment with HD restored the basal levels (F). Protein lysates were also incubated with a β-actin antibody (G) or laminin antibody (B) in order to verify that all samples had been loaded in equal quantities. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from N = 5 mice/group. (A) *** p < 0.001 vs. Sham; ** p < 0.01 vs. rotenone; (C) *** p < 0.001 vs. Sham; ** p < 0.01 vs. rotenone; (D) *** p < 0.001 vs. Sham; ** p < 0.01 vs. rotenone; (E) ** p < 0.01 vs. Sham; ** p < 0.01 vs. rotenone; (F) *** p < 0.001 vs. Sham; *** p < 0.01 vs. rotenone.