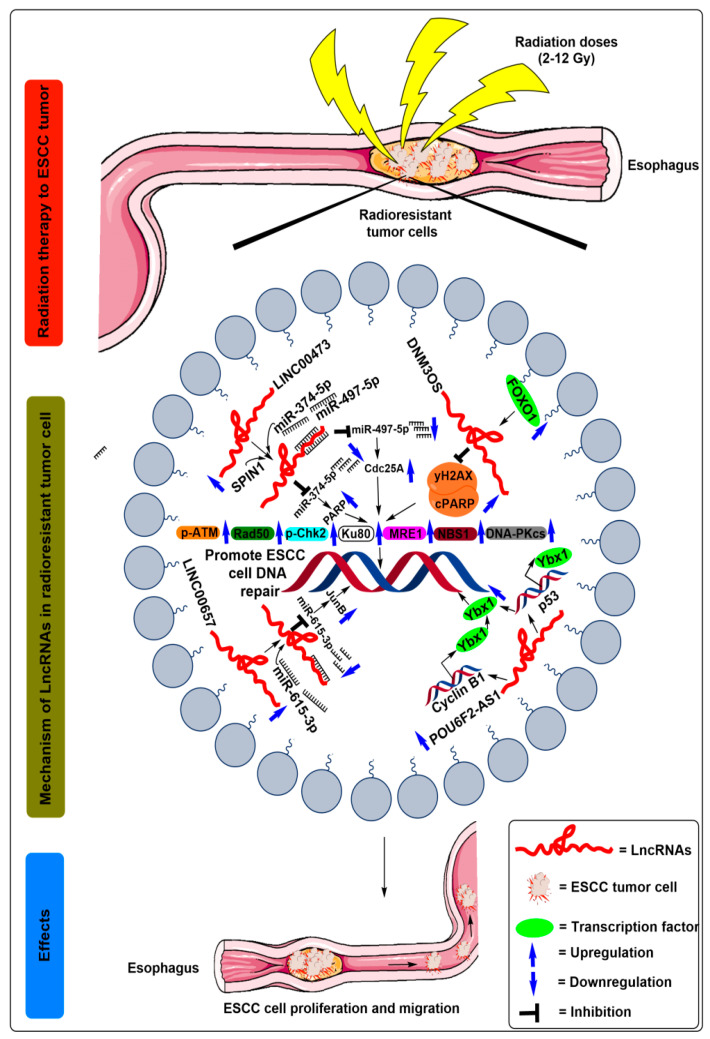
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the molecular mechanisms of lncRNAs in the regulation of radioresistance in ESCC treatment. After radiation exposure to the ESCC cells, increased expression of FOXO1 transcribes the lncRNA DNM3OS by binding to its promoter region. Moreover, the increased expression of DNM3OS suppressed the levels of double-strand break proteins, such as H2A histone family member X (γH2AX) protein and cleaved poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) followed by increased levels of DNA repair enzymes, such as pATM, Rad50, phosphorylated checkpoint kinase 2 (pChk2), Ku80, meiotic recombination 11 homolog 1 (MRE1), Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 (NBS1), DNA protein kinase (DNA-PKcs), and ultimately promote ESCC cell DNA repair. After radiation exposure to the ESCC cells, SPIN1, miR-374-5p, and miR-497-5p demonstrated competitive binding to upregulated lncRNA LINC00473. Moreover, miR-374-5p and miR-497-5p was suppressed after binding to the LINC00473, which is followed by the upregulated expression of PARP and Cdc25A, respectively, which are ultimately unable to break the double-strand DNA of ESCC cells. After radiation exposure to the ESCC cells, miR-615-5p competes for its binding to the upregulated lncRNA LINC00657. Moreover, the expression of miR-615-5p was suppressed after binding to the LINC00657, which is followed by the upregulated expression of JunB, which ultimately promotes the double-strand DNA repair of ESCC cells. After radiation exposure to the ESCC cells, POU6F2-AS1 expression was increased, which further recruits Ybx1 to the promoters of cyclin B1 (CCNB1) and p53 gene and the DNA damage sites and thus increases the Ybx1 protein levels, which ultimately promotes ESCC cell DNA repair.