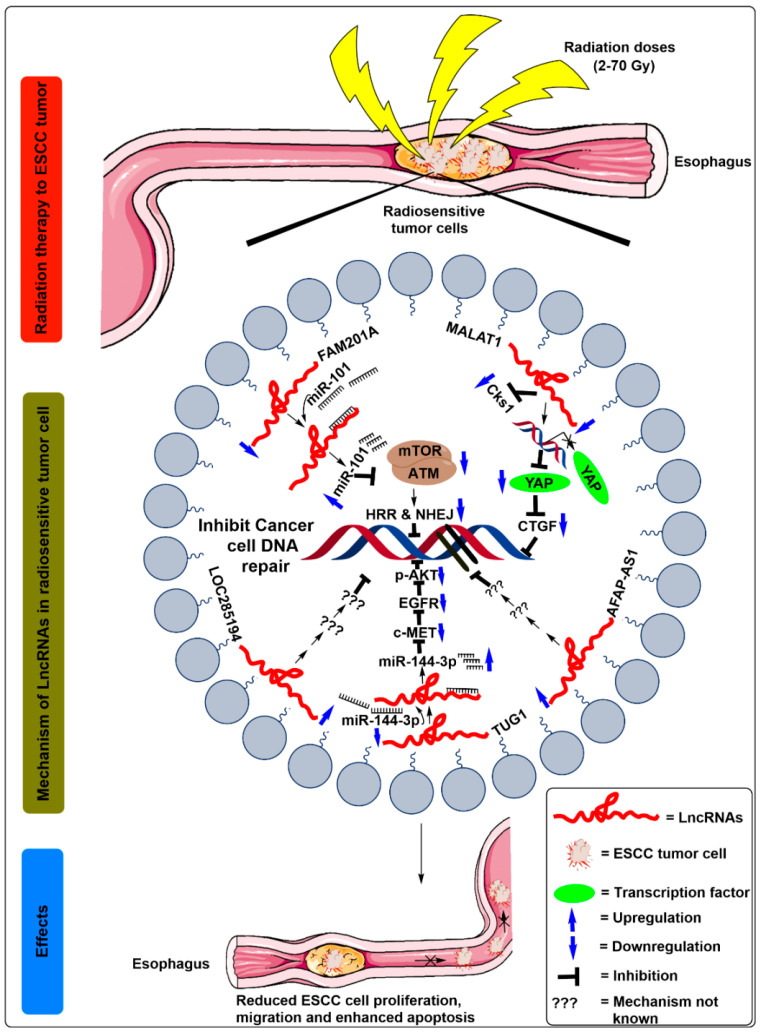
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of the molecular mechanisms of lncRNAs in the regulation of radiosensitivity in ESCC treatment. After radiation exposure to the ESCC cells, miR-101 binds to downregulate lncRNA FAM201A. Moreover, the expression of miR-101 was increased after binding to the FAM201A, which is followed by downregulated expression of mTOR and ATM, which decreases the homologous recombination repair (HRR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway and thus promotes the breakdown of double-strand DNA of ESCC cells. After radiation exposure to the ESCC cells, MALAT1 expression was decreased, which further inhibits Cks1 levels at both mRNA and protein levels. In addition, it also decreased YAP’s translational activity, reducing the expression levels of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), thus enhancing the breakdown of the double-strand DNA in ESCC cells. After radiation exposure to the ESCC cells, downregulated expression of lncRNAs LOC285194 and AFAP-AS1 inhibits DNA repairing of ESCC cells. After radiation exposure to the ESCC cells, miR-144-3p competes with binding to the downregulated lncRNA TUG1. Moreover, the expression of miR-144-3p was increased after binding to the TUG1, which is followed by downregulated expression of c-MET, EGFR, and p-Akt protein, which ultimately promotes the breakdown of double strand DNA of ESCC cells and confers radiosensitivity.