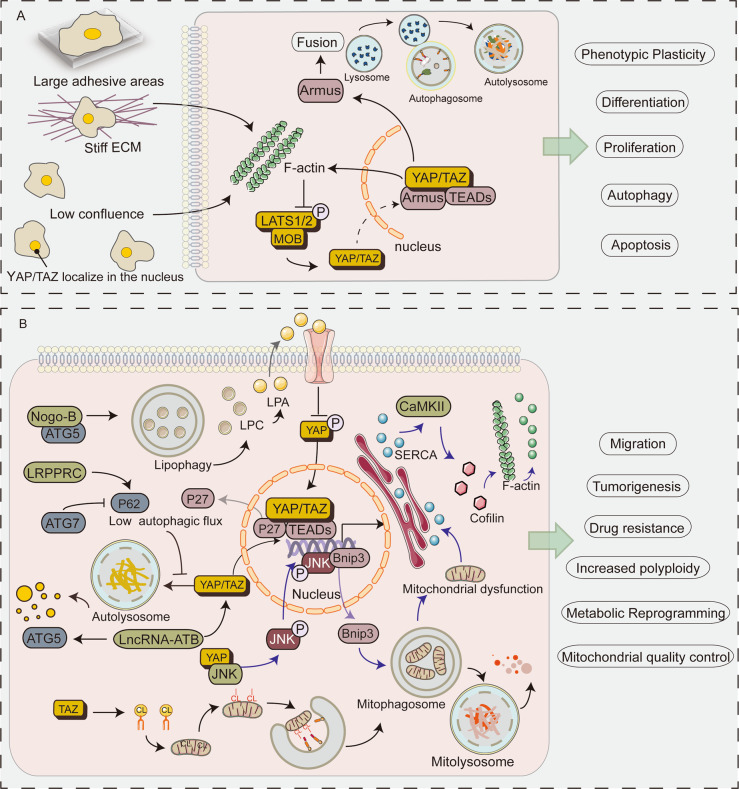
Fig. 4. Schematic diagram showing the role of YAP and TAZ in autophagy.
A When cells are at low density and on a stiff extracellular matrix (ECM), F-actin level is elevated leading to activation and nuclear import of YAP/TAZ, and upregulation of YAP/TAZ targets (such as myosin II and Armus). Activation of YAP/TAZ promotes F-actin accumulation. Cell mechanics control autophagic flux by regulating the transcriptional activity of YAP/TAZ. The YAP/TAZ-autophagy axis regulates a series of biological processes, such as proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation and phenotypic plasticity. B Loss of Atg7 or LRPPRC decreases autophagic flux. As an autophagic substrate, YAP cannot be degraded by autophagy, which increases nuclear localization of YAP. Activated YAP triggers accumulation of p27, which in turn leads to cellular polyploidy. lncRNA-ATB influence autophagy by participating in the transcriptional regulation of ATG5. In addition, lncRNA-ATB promotes autophagy by regulating YAP activation. Nogo-B interacts with ATG5 to promote lipophagy leading to LPC-dependent inhibition of YAP phosphorylation and enhances the oncogenic activity of YAP. YAP promotes metastasis via the mitophagy-SERCA-CaMKII pathways and cofilin/F-actin/lamellipodium axis. YAP binds to JNK in the cytoplasm, inducing JNK phosphorylation and nuclear localization, enhancing Bnip3 transcriptional activity. The Bnip3-induced mitophagy leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and ATP deficiency. Insufficient ATP inactivates SERCA and triggers [Ca2+]i overload; [Ca2+]i which phosphorylates CaMKII and inactivates cofilin, ultimately leading to F-actin degradation and abrogation of lamellipodium-based migration. Cardiolipin (CL) is a phospholipid found in the inner mitochondrial membrane. TAZ is required for catalyzation of CL. When mitochondria are damaged, cardiolipin is externalized and LC3 contains CL-binding sites to initiate mitophagy, thereby maintaining mitochondrial quality control. CaMKII, Ca/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases ΙΙ; CL, cardiolipin; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; SERCA, sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase.