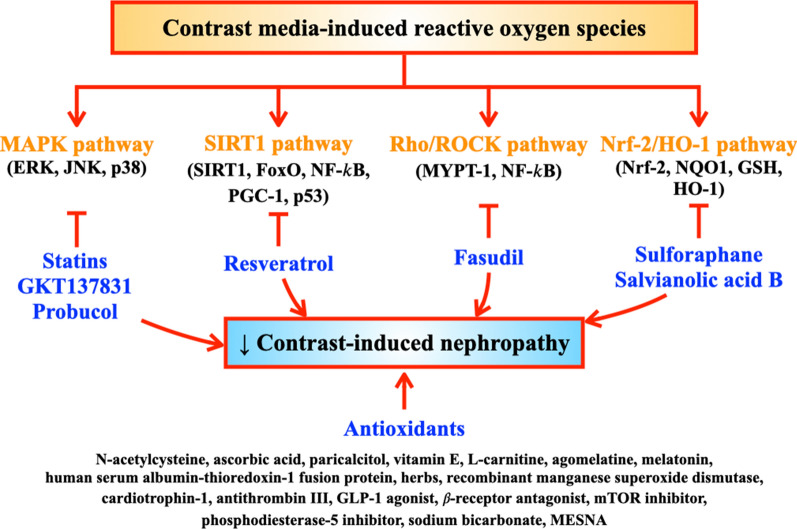
Fig. 3.
Intervention to reduce ROS for the prevention of CIN: evidence from in vitro, in vivo and clinical studies. In response to the mechanisms involved in ROS production in CIN, interventions to reduce ROS via complex pathways are illustrated. The MAPK pathway was inhibited by statins, GKT137831 and probucol. The SIRT1 pathway was inhibited by resveratrol. Rho/ROCK pathway was inhibited by fasudil. The Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway was inhibited by sulforaphane and salvianolic acid B. Antioxidant agents reported to exert benefits in CIN prevention have also been shown in this figure. CIN, contrast-induced nephropathy; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MESNA, sodium-2-mercaptoethane sulphonate; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; Nrf-2/HO-1, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase 1; ROCK, rho-kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SIRT1, silent information regulator