Figure 1.
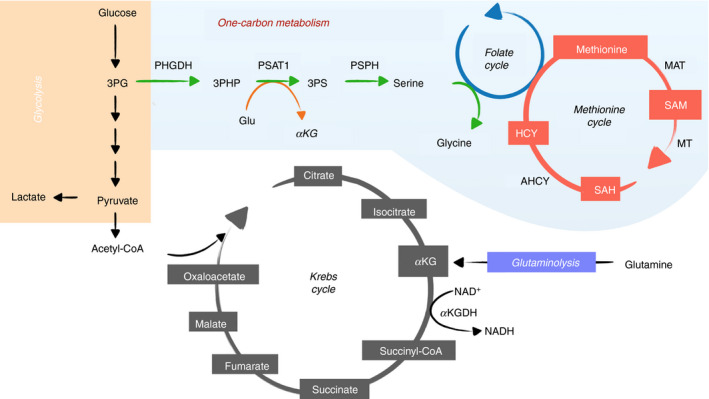
Metabolic pathways that provide metabolic substrates for epigenetic cycle. Glycolysis (orange), involves the enzymatic catabolism of glucose to pyruvate and lactate in the cytoplasm. Pyruvate can be converted to acetyl‐CoA in mitochondria and shuttled through several enzymatic reactions of the Krebs cycle (gray) to generate metabolic intermediates. Glutamine through glutaminolysis (purple) can be metabolized to α‐ketoglutarate in the Krebs cycle. Intermediates from glucose catabolism during glycolysis can branch out through the serine one‐carbon metabolism (blue) to generate amino acids of serine and glycine fueling into the folate and methionine cycle to generate S‐adenosyl‐methionine. 3PG, 3‐phosphoglycerate; 3PHP, 3‐phosphohydroxypyruvate; 3PS, 3‐phosphoserine; PHGDH, phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PSAT1, phosphoserine aminotransferase 1; PSPH, phosphoserine phosphatase; MAT, methionine adenosyltransferase; SAM, S‐adenosyl‐methionine; MT, methyltransferase; SAH, S‐adenosylhomocysteine; HCY, homocysteine; AHCY, S‐adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase; αKG, α‐ketoglutarate; KGDH, α‐ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
