Figure 1.
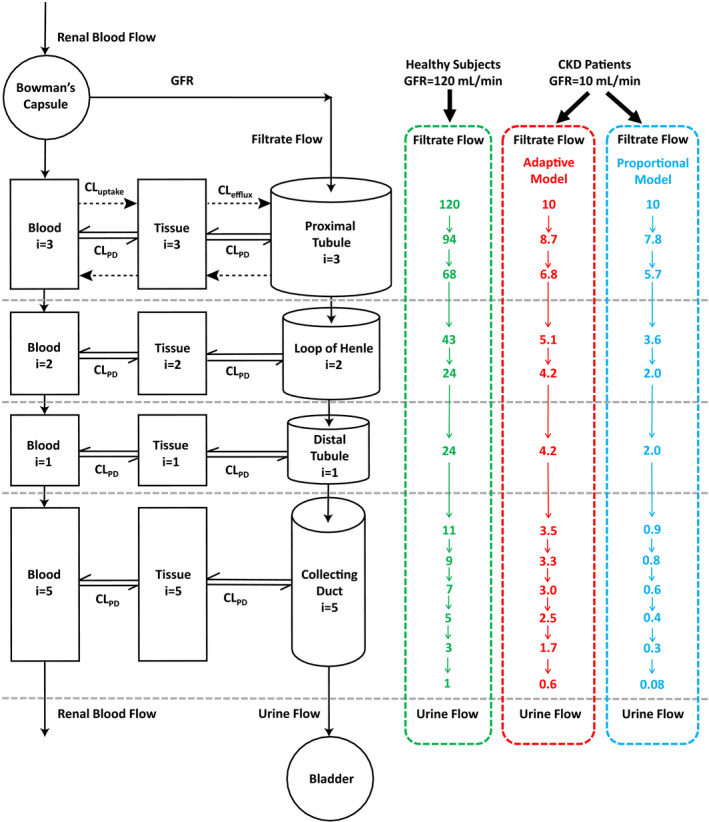
Schematic presentation of the mechanistic kidney model structure, together with the corresponding renal tubular flow rate (TFR; in mL/min) for each individual tubular subsegment (a total of 12) of the model. Three sets of physiologically‐based TFR shown here are for healthy subjects (glomerular filtration rate (GFR) 120 mL/min, in green) and for the representative patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) who have residual GFR of 10 mL/min using the adaptive model (in red) and the proportional model (in blue). The dynamic physiologically‐based mechanistic kidney model shown here is parameterized by 33 volume parameters, 22 surface area parameters, 12 peritubular renal blood flow parameters, 12 renal TFR parameters, 3 basolateral uptake clearance parameters, and 3 apical efflux clearance parameters to fully capture the disposition of drugs/metabolites between renal tubules, cells, and vasculature. CL, clearance.
